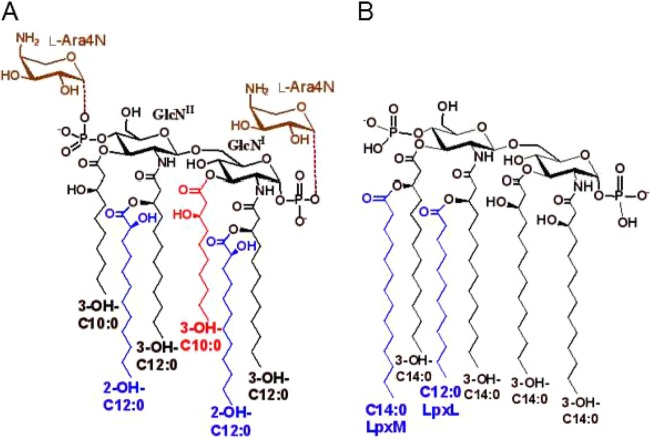
FIG 3.
Lipid A structure. (A) P. aeruginosa lipid A with potential modification that include: cleavage of the 3-O-acyl chain (3-OH-C10:0, red), addition of 1 or 2 l-Ara4N moieties (brown), and 2-hydroxylation of one or both of the secondary acyl chains (blue). (B) Typical E. coli lipid A. The secondary acyl chains (blue) are added by LpxL (C12:0) and LpxM (C14:0) as indicated. The loss of either or both of these acyl chains results in antibiotic hypersusceptibility phenotypes.