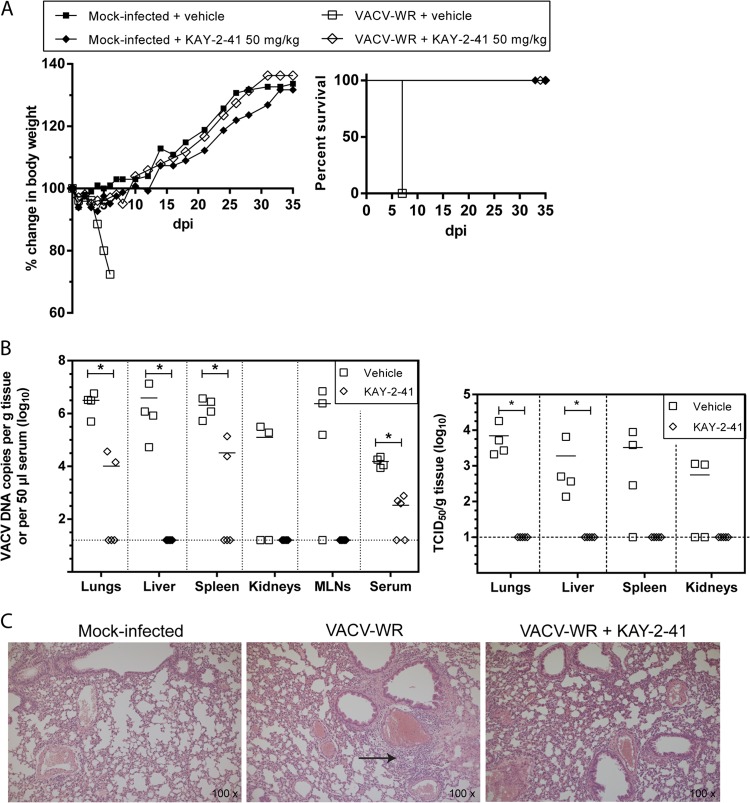
FIG 5.
KAY-2-41 treatment inhibits virus dissemination and replication in various organs. (A) Body weight evolution and survival curves of mock-infected and VACV-WR-infected mice that received vehicle (PBS) or KAY-2-41 treatment at 50 mg/kg once a day for 5 consecutive days beginning 6 h after virus exposure. Body weight evolution is shown as the percentage of the change in average weight for each group of mice (5 mice per group). dpi, day postinfection. (B) Viral DNA loads in various organs and in serum (left) and virus titers in lungs, liver, spleen, and kidneys (right) are shown. Animals were sacrificed at day 5 p.i. Viral loads were determined by qPCR and are expressed as VACV DNA copy numbers per g of tissue or per 50 μl of serum. Virus titers are shown in TCID50s per g tissue. The scatter plots show the viral DNA loads or virus titers from individual mice and the means (horizontal bars) for each group. Four (VACV-WR-infected) or five (VACV-WR-infected and KAY-2-41-treated [50 mg/kg]) individual mice were used lung. MLNs, mesenteric lymph nodes. Dashed lines, limit of detection. The viral DNA loads or virus titers of KAY-2-41-treated mice differed significantly from those of the PBS-treated group by the Mann-Whitney test (*, P < 0.05). (C) Lung tissue examination at 5 days p.i. While VACV-WR-treated mice exhibited interstitial inflammation (arrow), no inflammatory cells were seen after KAY-2-41 treatment.