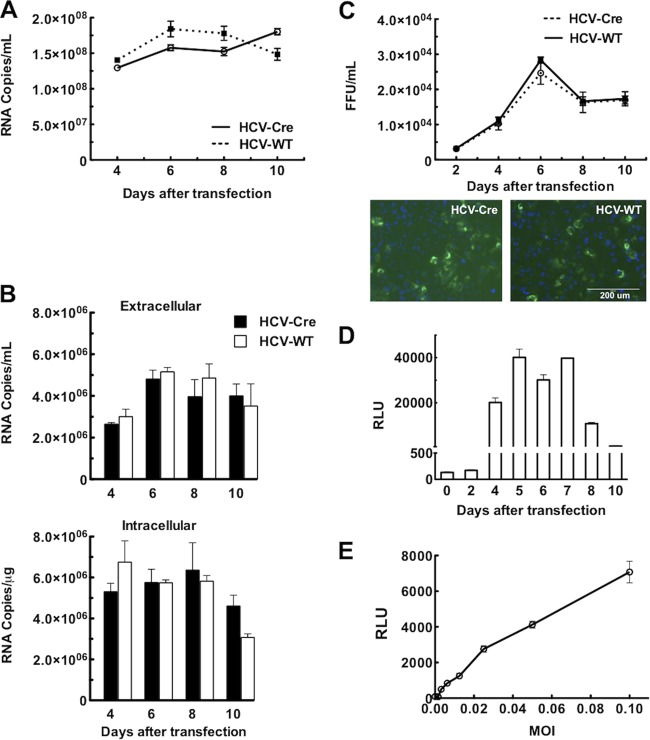
FIG 2.
HCV-Cre and HCV-WT replicate and infect similarly in Huh7.5.1 cells. (A) HCV RNA levels from culture media collected at various times following transfection of in vitro-transcribed HCV-Cre or HCV-WT RNA were quantified by real-time PCR analysis. The amount of HCV in the media is expressed as copy numbers of HCV RNA/ml. (B) Naive Huh7.5.1 cells plated in 12-well plate were infected with 100 μl of HCV-Cre and HCV-WT media collected at various times following transfection. Total RNAs were isolated from both the media and cells at 48 h after infection. The HCV RNA was quantified by real-time PCR analysis. (C) Naive Huh7.5.1 cells plated on 96-well plates were inoculated with serial dilutions of culture supernatant collected at various times following HCV RNA transfection, as indicated. After 3 days, the cells were processed for HCV core immunofluorescent staining (examples are shown below). HCV core-positive foci were counted, and the number of FFU of each virus was calculated as FFU/ml. (D) Induction of Gluc activity in LoxPGluc cells following HCV-Cre infection. Huh7.5.1.LoxPGLuc cells plated on 96-well plates were inoculated with HCV-Cre-containing medium (10 μl/well) harvested at various times following HCV-Cre mRNA transfection. The Gluc activity, defined as relative luciferase units (RLU), of the cultured medium was measured at 48 h after HCV-Cre infection. The data at each time point are means and standard errors of the mean (SEM) from 5 replicates. (E) Correlation between the multiplicity of infection (MOI) of HCV-Cre and Gluc activities. Huh7.5.1.LoxPGLuc cells plated on 96-well plates were inoculated with various titers (MOI) of HCV-Cre as indicated. Forty-eight hours after HCV-Cre infection, 10 μl of culture medium was transferred to an assay plate, and the Gluc activity was measured. The data are means ± SEM from 5 replicates.