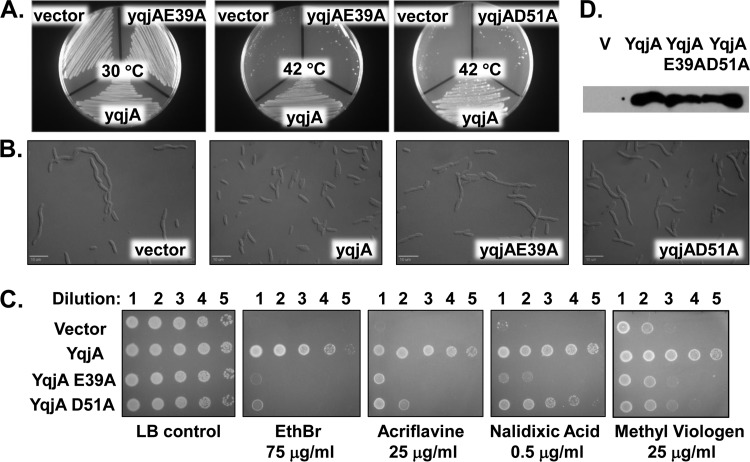
FIG 2.
Mutation of YqjA E39 or D51 abolishes the ability to restore growth, cell division, or drug resistance to BC202. (A) BC202 transformed with pBAD, pBAD-yqjA, pBAD-yqjA(E39A), or pBAD-yqjA(D51A) was grown at 30°C (left) or 42°C (center and right). Wild-type YqjA, but not point mutants, restores growth to BC202 at 42°C. BC202/pBAD-yqjA(D51A) also grew at 30°C (not shown). (B) Micrographs of BC202 transformed with pBAD, pBAD-yqjA, pBAD-yqjA(E39A), or pBAD-yqjA(D51A) and grown at 30°C. Wild-type YqjA, but not point mutants, restores normal cell division to BC202. Bar, 10 μm. (C) Sensitivity of BC202 transformed with control vector, cloned yqjA, yqjA(E39A), or yqjA(D51A) to EthBr (75 μg/ml), acriflavine (25 μg/ml), nalidixic acid (0.5 μg/ml), and methyl viologen (25 μg/ml). All strains grew on LB plates without biocides at 30°C. Wild-type YqjA, but not point mutants, restores drug resistance to BC202 at 30°C. (D) Expression of yqjA, yqjA(E39A), and yqjA(D51A) in membrane fractions as determined by Western blotting with antihexahistidine antibody. All growth was carried out in LB-Amp supplemented with 0.002% (A and C) or 0.1% (B and D) arabinose.