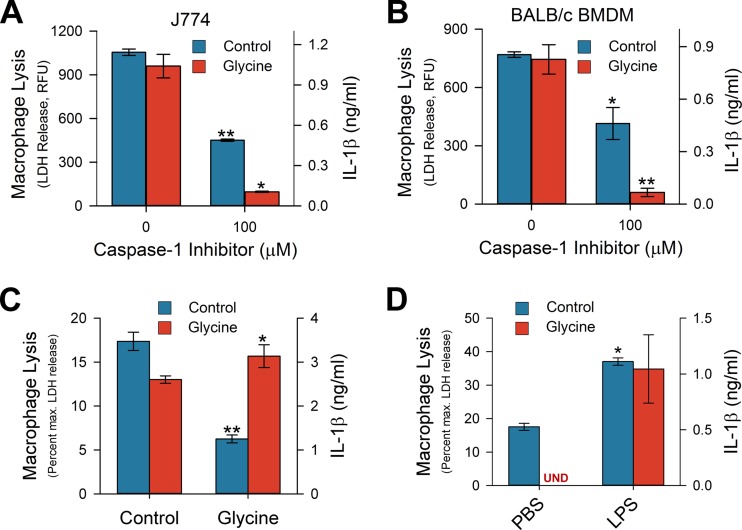
FIG 1.
C. albicans-induced macrophage lysis has characteristic features of pyroptosis. (A and B) J774 macrophages (A) or bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDM) from BALB/c mice (B) were treated with the caspase-1 inhibitor z-YVAD-fmk or carrier, prestimulated with LPS for 2 h, and then exposed to C. albicans at an MOI of 2:1 for 5 h. LDH (blue) and IL-1β (red) were measured from the supernatant of the coculture. LDH release was measured using a fluorogenic assay; data are presented as mean relative fluorescence units (RFU). (C) LPS-stimulated J774A.1 macrophages were exposed to C. albicans in the presence or absence of 5 mM glycine and evaluated as described above. (D) J774 macrophages were prestimulated with LPS (50 ng/ml) or PBS as a control and exposed to C. albicans as described above. LDH activity of supernatants (C and D) is expressed as a percentage of the maximum LDH release measured from an identical sample of detergent-treated macrophages. Each experiment was performed at least twice with similar results, and a representative single experiment is shown. Bar heights are the means of least three technical replicates, and error bars indicate standard deviations. Data were analyzed by Student's t test: **, P ≤ 0.001 compared to control; *, P ≤ 0.05 compared to control. UND, undetectable.