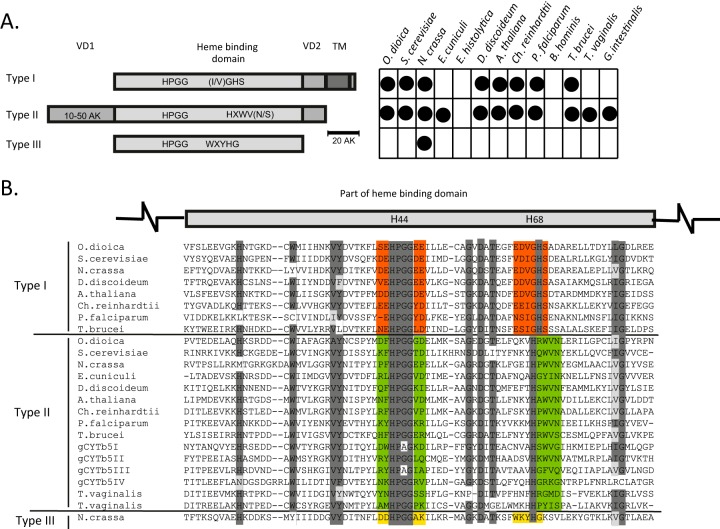
FIG 1.
The three groups of cytb5 proteins. (A) Schematic representation of the structural differences between the canonical group I cytb5, group II soluble cytb5, and fungal group III cytb5 proteins. The chart indicates the distribution of cytochromes in representative eukaryotes. VD, variable domain; TM, transmembrane domain. O. dioica, Oikopleura dioica; S. cerevisiae, Saccharomyces cerevisiae; N. crassa, Neurospora crassa; E. cuniculi, Encephalitozoon cuniculi; D. discoideum, Dictyostelium discoideum; A. thaliana, Arabidopsis thaliana; Ch. reinhardtii, Chlamydomonas reinhardtii; P. falciparum, Plasmodium falciparum. (B) Alignment of partial heme-binding domains. The two histidine residues that are critical for heme iron coordination are highlighted in the schematic above the alignment. Highly conserved regions are shaded in dark gray, and similar amino acids in conserved regions are shaded in light gray. Red, green, and yellow highlight typical motifs for each type of cytb5.