FIG 5.
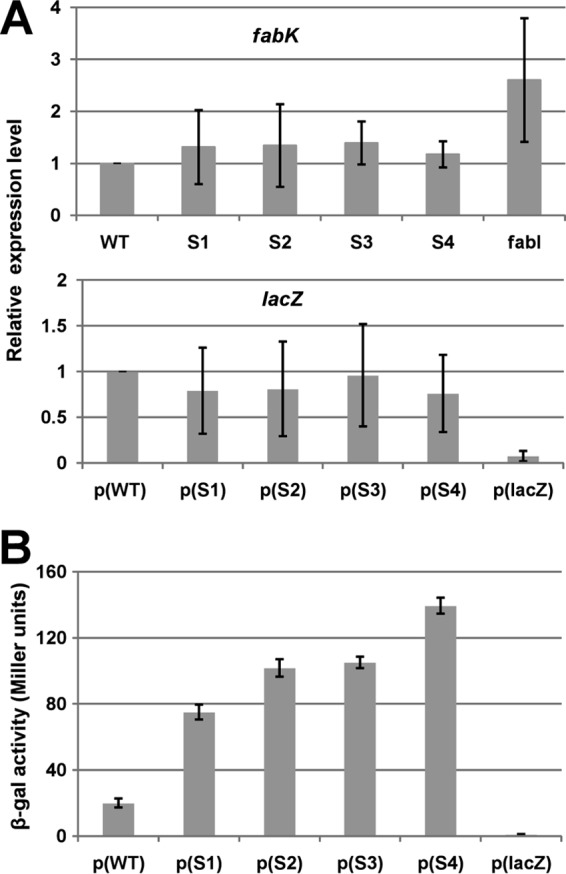
Effects of the spontaneous mutations on fabK transcription and translation. (A) qRT-PCR analyses of the effects on fabK and lacZ transcription. Transcription of fabK was analyzed in the wild-type strain and the spontaneous mutant strains, whereas lacZ transcription was analyzed for the wild-type strains carrying the translational fusion plasmid. Cells were grown in GM17 medium to mid-log phase, and RNA was isolated as described in Materials and Methods. The qRT-PCR data were from no less than four independent tests and are expressed as means ± standard deviations. The p(lacZ) designation denotes the promoterless ′lacZ vector. (B) Effects of the spontaneous mutations on β-galactosidase expression from a plasmid carrying a P32::fabK::lacZ translational fusion. The wild-type strain FA2-2 carrying the fusion plasmids was grown in GM17 medium to mid-log phase, and β-galactosidase activities were measured from more than three independent experiments. The error bars indicate standard deviations. p(WT), p(S1), p(S2), p(S3), p(S4), and p(lacZ) indicate fusion plasmids pBHK323, pBHK324, pBHK325, pBHK326, pBHK327, and pBHK322 carrying the −136 to +35 fragments of wild-type fabK, one of the four spontaneous fabK mutants, or the empty ′lacZ vector, respectively.
