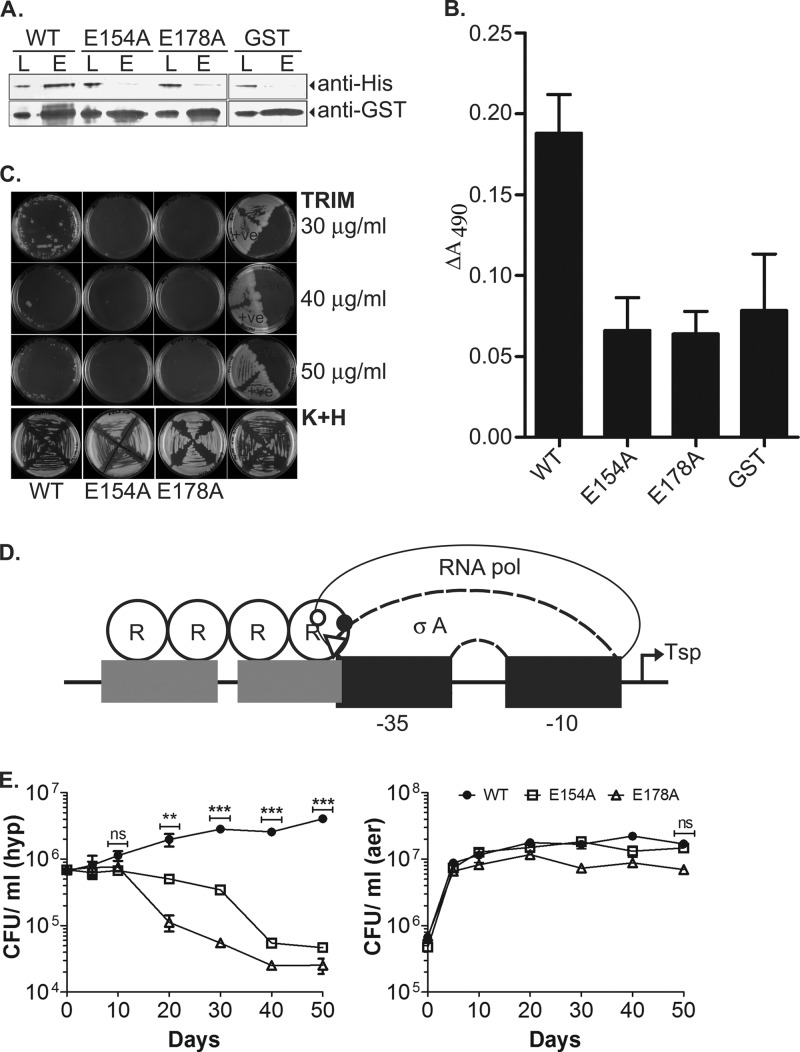
FIG 5.
Interaction of DevR with SigA and effect on M. tuberculosis viability. (A) GST pulldown assay using SigA and GST-DevR/GST proteins. L, input load; E, elution. Monoclonal antibodies anti-GST (1:5,000; Sigma) and anti-His6 (1:2,000; Sigma) were used for the detection of DevR/GST and SigA proteins, respectively, by Western blotting. (B) ELISA using proteins DevR, E154A, E178A, GST tag only and SigA. ΔA490 values were obtained after subtracting the absorbance values obtained for control wells coated with BSA protein. (C) MPFC assay to analyze in vivo interaction of M. tuberculosis DevR and SigA. M. smegmatis transformants were subcultured on 7H11 agar containing Kan, Hyg, and Trim and incubated at 37°C for 3 to 6 days. (D) Model of interaction of DevR surface residues E154 (solid circle) and E178 (triangle) with SigA. R155 and K208 residues on DevR that are likely to interact with RNA polymerase (not excluding SigA) are shown by an empty circle. (E) Survival of M. tuberculosis WT and mutant strains. The viability of M. tuberculosis strains was assessed under aerobic and hypoxic conditions over a period of 50 days. The mean CFU ± SD determined from three independent cultures is shown. The difference in hypoxic viability between the WT and the E154A and E178A mutants was statistically significant on days 20 (**, P < 0.005) and 30, 40, and 50 (***, P < 0.0005).