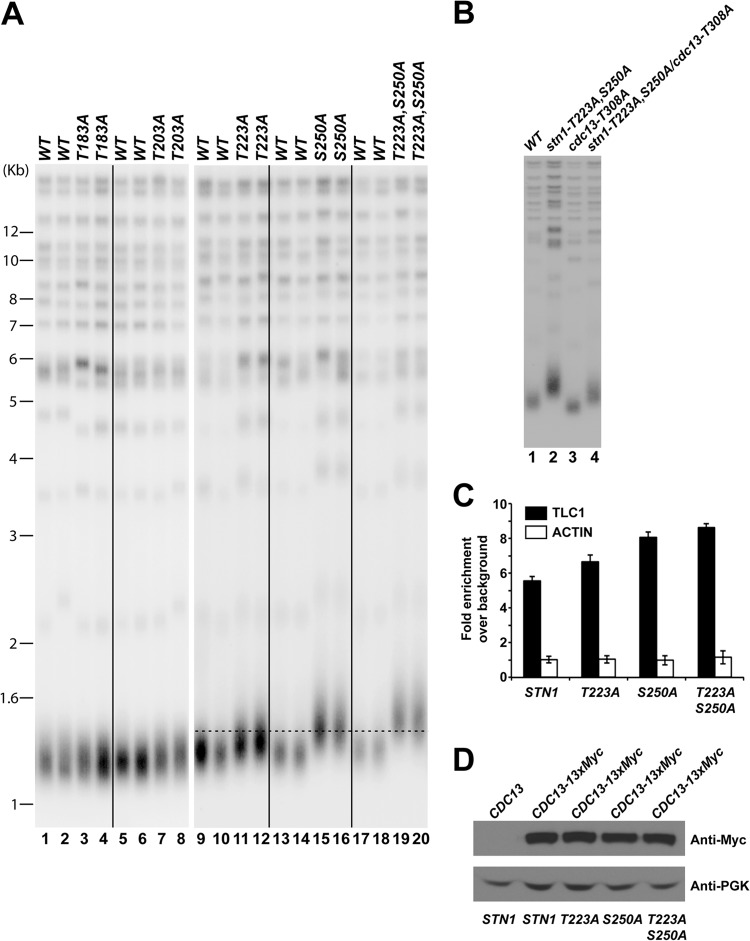
FIG 3.
Mutations in STN1 phosphorylation sites cause telomere elongation in vivo. (A) Only mutation of STN1 threonine 223 or serine 250 to alanine results in telomere elongation. Double mutations of both threonine 223 and serine 250 to alanines result in further telomere lengthening. (B) Yeast cells that contain both the CDC13 and STN1 phosphorylation site mutations exhibit an intermediate telomere length phenotype compared to CDC13 or STN1 mutant alone. (C) Enhanced efficiency of telomerase recruitment by Cdc13 in STN1 phosphorylation mutants, as shown by an increased association between Cdc13 and TLC1 in coimmunoprecipitation experiments followed by real-time qRT-PCR (TLC1, RT-PCR primers for specific amplification of TLC1 RNA; actin, RT-PCR primers for specific amplification of actin mRNA as negative control). The data are derived from three independent experiments. (D) Straight Western blotting shows that the expression of Cdc13-13×Myc is not affected by stn1 phosphorylation mutations in vivo.