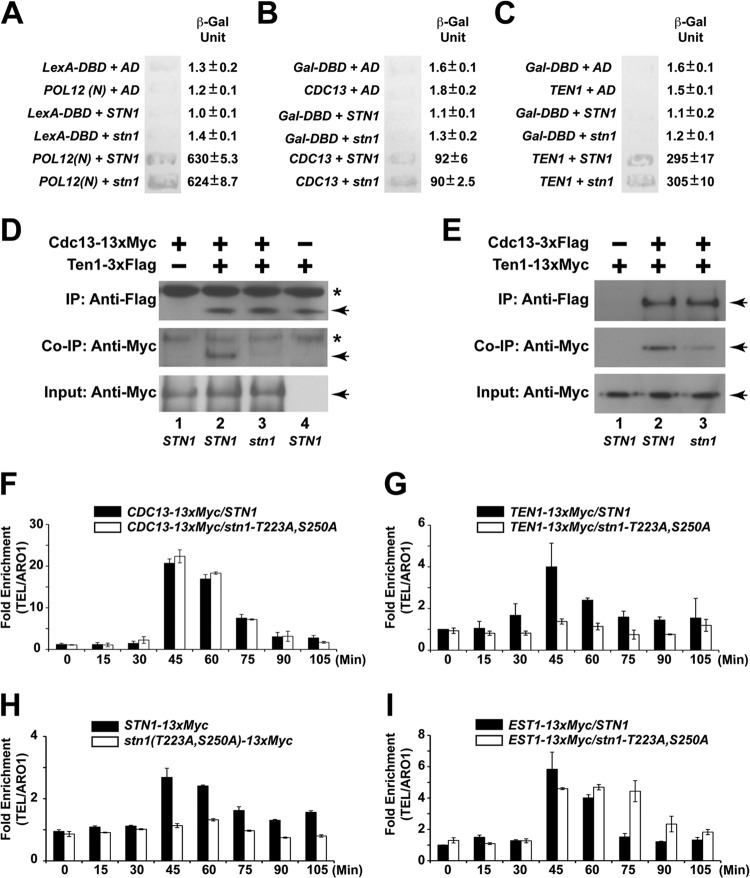
FIG 6.
Cdk1-dependent phosphorylations of Stn1 are essential for the recruitment of the CST complex to the telomere. (A) Stn1 phosphorylations are not necessary for the interaction between Stn1 and Pol12, as shown by the yeast two-hybrid assay. (B) Stn1 phosphorylations are not necessary for the interaction between Stn1 and Cdc13, as shown by the yeast two-hybrid assay. (C) Stn1 phosphorylations are not necessary for the interaction between Stn1 and Ten1, as shown by the yeast two-hybrid assay. LexA-DBD, LexA DNA-binding domain alone; AD, Gal4 activation domain alone; POL12(N), POL12 N-terminal 381 amino acids fused to the LexA DNA-binding domain; Gal-DBD, Gal4 DNA-binding domain alone; CDC13, CDC13 with deletion in the DNA-binding domain fused to Gal4 DNA-binding domain; TEN1, full-length wild-type TEN1 fused to Gal4 DNA-binding domain; STN1, full-length wild-type STN1 fused to Gal4 activation domain; stn1, full-length stn1-T223A,S250A mutant fused to Gal4 activation domain. (D) Coimmunoprecipitation (Co-IP) of Cdc13-13×Myc and Ten1-3×Flag is dramatically reduced in the stn1-T223A,S250A mutant yeast strain compared to the STN1 yeast strain. The asterisks denote nonspecific bands in the background. The Cdc13-13×Myc and Ten1-3×Flag proteins are marked by the arrows. (E) Coimmunoprecipitation of Ten1-13×Myc and Cdc13-3×Flag is dramatically reduced in the stn1-T223A,S250A mutant yeast strain compared to the STN1 yeast strain. The Ten1-13×Myc and Cdc13-3×Flag proteins are marked by the arrowheads. (F) ChIP assays in synchronous yeast cultures show that the cell cycle-dependent recruitment of Cdc13 to the telomere is not affected in the stn1-T223A,S250A mutant. (G) ChIP assays in synchronous yeast cultures show that the cell cycle-dependent recruitment of Ten1 to telomere is dramatically reduced in the stn1-T223A,S250A mutant. (H) ChIP assays in synchronous yeast cultures show that the cell cycle-dependent recruitment of Stn1 to the telomere is dramatically reduced in the stn1-T223A,S250A mutant. (I) In contrast, ChIP assays in synchronous yeast cultures show the prolonged association of Est1 and the telomere in the stn1-T223A,S250A mutant.