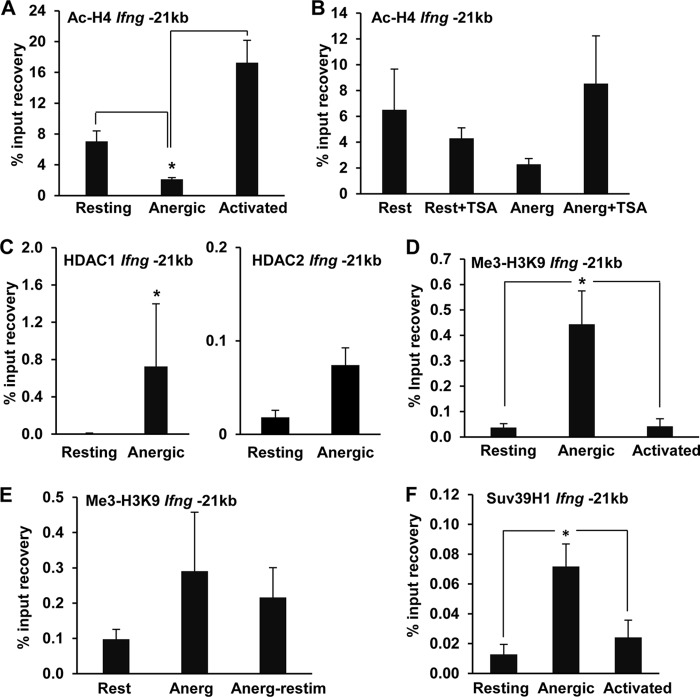
FIG 4.
Anergic TH1 cells show repressive histone modifications at the −21kb CNS. (A) H4 acetylation at the Ifng −21kb CNS was assessed by ChIP assay of resting, anergic, and activated TH1 cells by use of anti-acetyl H4 antibodies. Data are means and SEM for 4 independent experiments. *, P < 0.05. (B) H4 acetylation at the Ifng −21kb CNS was measured by ChIP assay of resting cells (Rest) and cells anergized (Anerg) in the presence or absence of the histone deacetylase inhibitor TSA (10 nM). Data are means and SEM for 2 independent experiments performed in triplicate. (C) HDAC1 and HDAC2 binding to the Ifng −21kb CNS in resting and anergic TH1 cells was determined by ChIP using an anti-HDAC1 or anti-HDAC2 antibody. Results are means and SEM for 3 and 2 independent experiments, respectively. *, P < 0.05. (D) Me3-H3K9 repressive chromatin modification at the Ifng −21kb CNS in resting, anergic (anti-CD3), and activated (anti-CD3 plus anti-CD28) TH1 cells was assessed by ChIP using an anti-Me3-H3K9 antibody. Results are means and SEM for 4 independent experiments. *, P < 0.05. (E) Stability of the Me3-H3K9 modification in anergic cells. Me3-H3K9 repressive chromatin modification at the Ifng −21kb CNS was determined by ChIP assay of resting, anergic TH1 cells and anergic cells restimulated for 24 h with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 antibodies. Data are means and SEM for 3 independent experiments. (F) Suv39H1 occupancy of the Ifng −21kb CNS was analyzed by ChIP using an anti-Suv39H1 antibody on resting, anergic, and stimulated cells. Bars represent means and SEM for 4 independent experiments. *, P < 0.05.