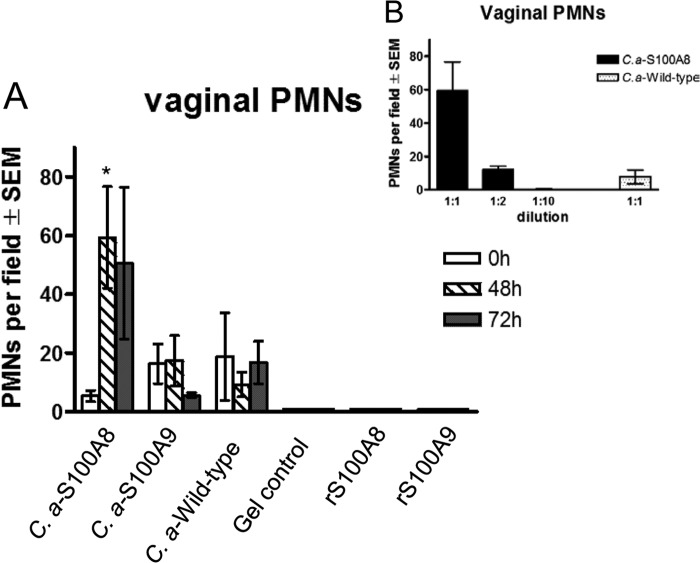
FIG 1.
In vivo PMN chemotactic ability of culture supernatants containing C. albicans-derived S100 alarmins. (A) PMN migration induced by S100 alarmins of C. albicans or E. coli origin. Overnight culture supernatants of S100A8, S100A9, and wild-type C. albicans were semisolidified with carboxymethylcellulose (3%) to reach a consistency of vaginal gel formulation. The vaginal gel preparations were administered intravaginally to estrogenized uninoculated mice once daily for 2 days in a volume of 20 μl per mouse using a microdispenser. Gel preparations of E. coli-derived recombinant S100A8 (rS100A8), S100A9 (rS100A9), or PBS (gel control) were tested in parallel. Vaginal lavage samples were collected prior to treatment and then daily after the last treatment. Vaginal PMNs were quantified by identifying PMNs by Pap smear staining and enumerating PMNs in 5 high-powered fields (×400 magnification) per mouse, and values were averaged. (B) Dose-dependent effects of S100A8-containing culture supernatant in vaginal PMN migration. Estrogenized uninoculated mice were treated with culture supernatant from S100A8-producing C. albicans at various dilutions. Vaginal lavage fluids were evaluated for PMNs at 48 h postadministration. The figure presents cumulative data from two repeats. *, P < 0.05 compared to the estrogenized untreated group (0 h). SEM, standard error of the mean.