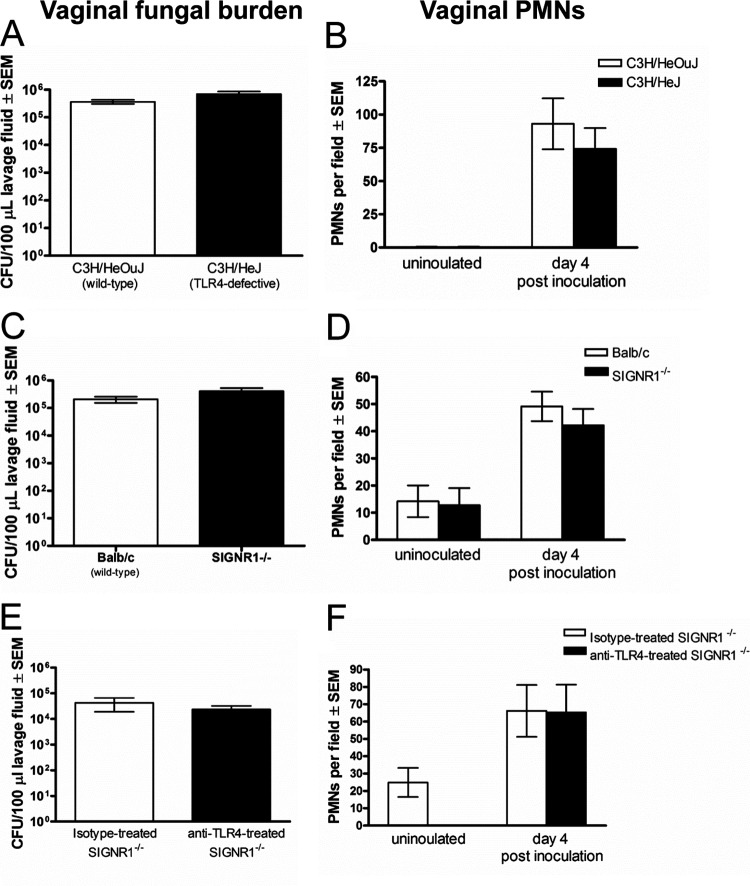
FIG 5.
Role of TLR4 and SIGNR1 in the PMN response following inoculation with C. albicans. (A and C) Quantification of vaginal Candida burden. The numbers of CFU per 100 μl of lavage fluids from estrogenized inoculated C3H/HeJ (TLR4-defective) (A), SIGNR1−/− (C) or appropriate wild-type strains of mice were assessed 4 days postinoculation. (B and D) Quantification of PMNs in vaginal lavage fluids. PMNs from estrogenized inoculated C3H/HeJ (TLR4-defective) (B), SIGNR1−/− (D), or the wild-type strains were identified by Pap smear staining and enumerated in 5 high-powered fields (magnification, ×400) per mouse and averaged. (E and F) Inoculation of TLR4-neutralized SIGNR1−/− mice with C. albicans. Estrogenized SIGNR1−/− mice were treated with anti-TLR4 or isotype control antibodies (100 μg/ml in PBS) in a volume of 20 μl at −4, 16, and 24 h postinoculation. Vaginal lavage fluids were collected on day 4 postinoculation, and vaginal fungal burden (E) and vaginal PMN migration (F) were assessed. The figure presents cumulative data from two or three repeat experiments with 6 to 10 mice per group. SEM, standard error of the mean.