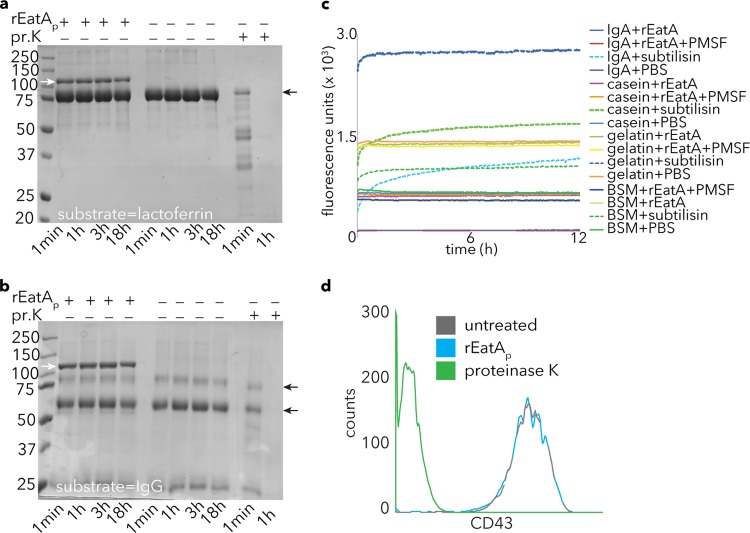
FIG 4.
Specificity of rEatAp activity. (a and b) EatA lacks the ability to degrade lactoferrin (a) or IgG (b). Proteinase K (pr.K) activity is shown as a positive control for each of these substrates in Coomassie blue-stained gel images. Small black arrows to the right of the gels indicate the respective substrate bands, while small white arrows in the leftmost lane show the migration of the rEatAp passenger domain. (c) Degradation of FITC-labeled substrates casein, BSM, gelatin, and IgA by the bacterial protease subtilisin (as evident by an increase in fluorescence) but not rEatAp. PMSF, phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride. (d) Fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) data demonstrating loss of mucin-like glycoprotein CD43 from the surfaces of Jurkat cells following proteinase K treatment but not rEatAp.