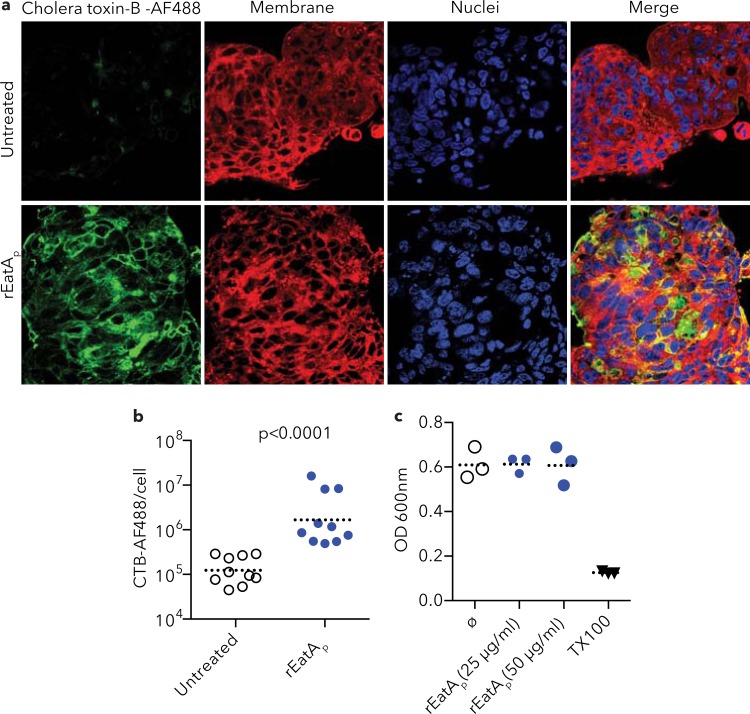
FIG 5.
rEatA treatment enhances cholera toxin binding to epithelial cells. (a) rEatAp treatment enhanced cholera toxin subunit B-Alexa Fluor 488 (AF488) conjugate (green) binding to LS174T cells (bottom row) compared to untreated cells (top row). (b) Quantification of signal intensity by Volocity software shows a significant increase in cholera toxin subunit B (CTB) binding to rEatAp-treated LS174T cells compared to untreated cells (P less than 0.0001). The dotted horizontal line shows the mean value for the group of mice. Each symbol represents the value for an individual mouse. (c) MTT cytotoxicity assay. rEatAp treatment of LS174T cells does not cause cellular toxicity (Triton X-100 [TX100] is shown as a positive control).