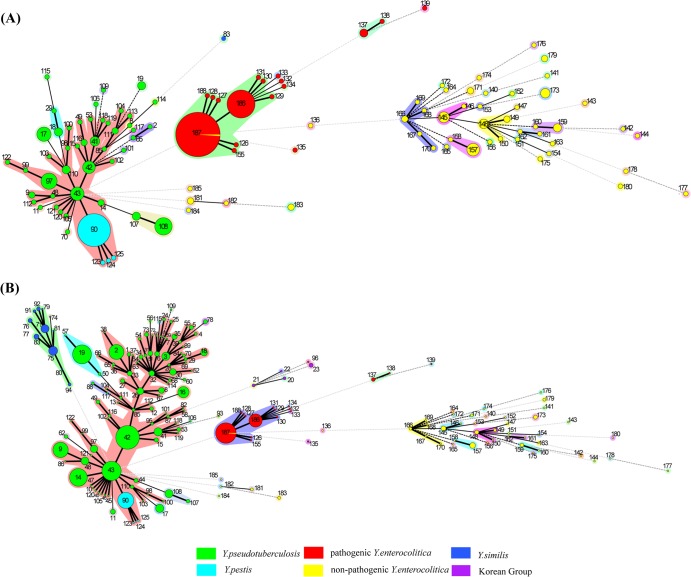
FIG 2.
Minimum spanning tree, colored by species, of three pathogenic Yersinia species before (A) and after (B) importing the UCC database sequences and combining them with 352 strains collected by our laboratory. Pathogenic Yersinia species fell into two distinct clusters; one included Y. pseudotuberculosis and Y. pestis, and the other involved pathogenic and nonpathogenic Y. enterocolitica strains. Y. pseudotuberculosis STs were numerous and scattering, Y. enterocolitica was relatively conserved, especially within pathogenic strains, and Y. pestis was the least diverse. The Arabic numerals show ST assignments. The circle sizes are directly proportional to the numbers of isolates. The numbers of locus differences are represented by bold lines (1 locus), plain lines (2 loci), black dotted lines (3 loci), dark-gray dotted lines (4 loci), and light-gray dotted lines (>5 loci). The colored shaded areas around the circles represent single-locus variants (SLVs).