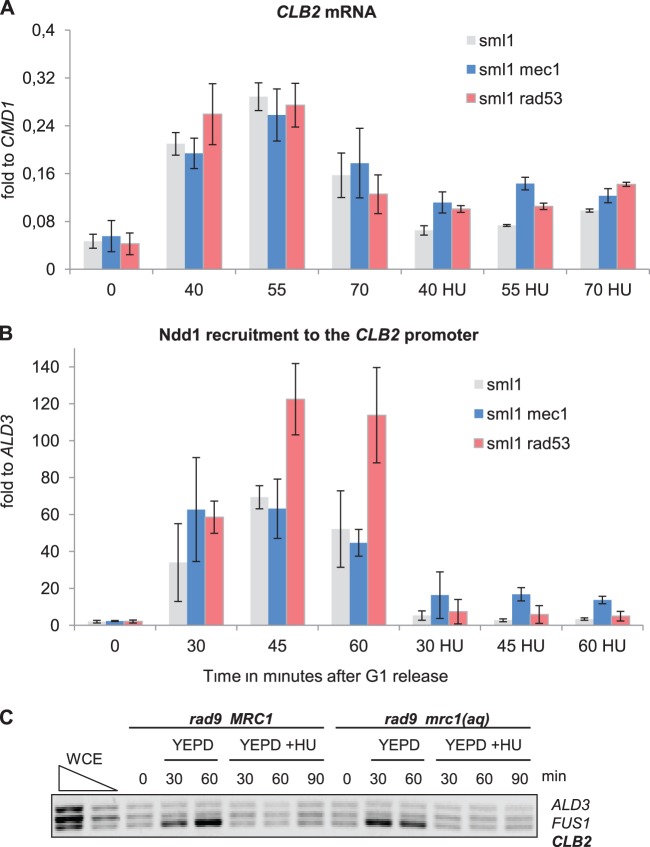
FIG 4.
HU-induced inhibition of G2/M-specific transcription is only partially dependent on the Mec1-Rad53 pathway. (A) Deletion of MEC1 could partially suppress HU-induced inhibition of mitotic gene transcription, whereas RAD53 deletion had only a lesser effect. Northern blotting was used to analyze CLB2 mRNA isolated from sml1 (JV754), sml1 mec1 (JV753), and sml1 rad53 (SKY324) cells released into YEPD with or without HU after G1 arrest. (B) The kinetics of Ndd1 recruitment to G2/M promoters are partially reestablished in HU-treated mec1 cells, whereas in the rad53 mutant, Ndd1 remains absent from the promoter. Ndd1-HA ChIP followed by qPCR analysis targeted to the CLB2 promoter was performed with the lysates of sml1 (SKY276), sml1 mec1 (SKY277), and sml1 rad53 (SKY324) cells released into YEPD with or without HU after G1 arrest. (C) Deletion of either RAD9 or MRC1 could not suppress HU-mediated inhibition of Ndd1 recruitment to G2/M promoters. Ndd1-HA ChIP followed by conventional multiplex PCR analysis was performed with the lysates of mrc1 rad9 cells expressing either MRC1 (SKY301) or mrc1AQ (SKY303) released into YEPD with or without HU after G1 arrest. ALD3 and FUS1 promoter-specific primers were used as negative controls. In all panels, error bars indicate standard deviations in at least three independent experiments. WCE, whole-cell extract.