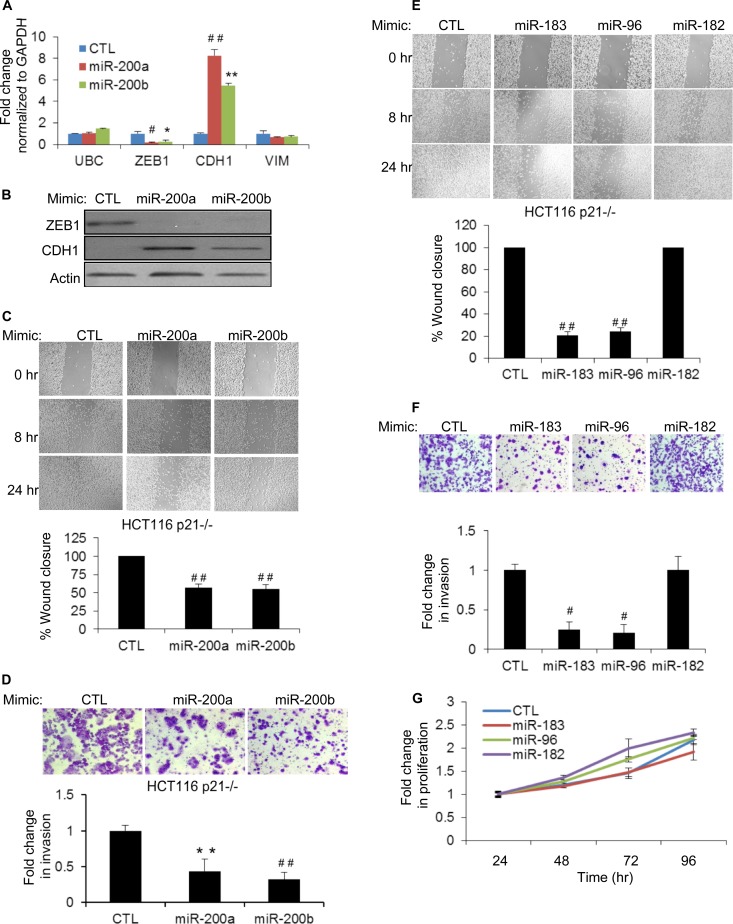
FIG 7.
Overexpression of miR-200, miR-183, or miR-96 inhibits migration and invasion in p21 knockout cells. (A) The effect of miR-200a or miR-200b overexpression in HCT116-p21−/− cells on the levels of ZEB1, CDH1, and VIM mRNAs was assessed by RT-qPCR after transfecting CTL, miR-200a, or miR-200b mimics for 48 h. The housekeeping gene UBC was used as a negative control. (B) Immunoblotting of ZEB1 and CDH1 after 48 h of transfection of CTL, miR-200a, or miR-200b mimics in HCT116-p21−/− cells. (C) Wound healing was monitored at the indicated time points in HCT116-p21−/− cells transfected 48 h earlier with CTL, miR-200a, or miR-200b mimics (top), and results from 3 experiments were quantitated by using ImageJ (bottom). (D, top) Representative pictures of invading HCT116-p21−/− cells 48 h after transfection with CTL, miR-200a, or miR-200b mimics. (Bottom) Results from 3 invasion assays were quantitated by using the ImageJ program. (E and F) Forty-eight hours after transfection of HCT116-p21−/− cells with CTL, miR-183, miR-96, or miR-182 mimics, the effect on cell migration (E) or invasion (F) was examined at the indicated time points by wound-healing assays (E) or Matrigel invasion assays (F). (G) The effect of introducing miR-183 cluster miRNAs on cell proliferation was determined by using Cell Counting Kit-8 from HCT116-p21−/− cells transfected with CTL, miR-183, miR-96, or miR-182 mimics. Error bars represent means ± standard deviations of three independent experiments. *, P < 0.05; #, P < 0.01; **, P < 0.005; ##, P < 0.001.