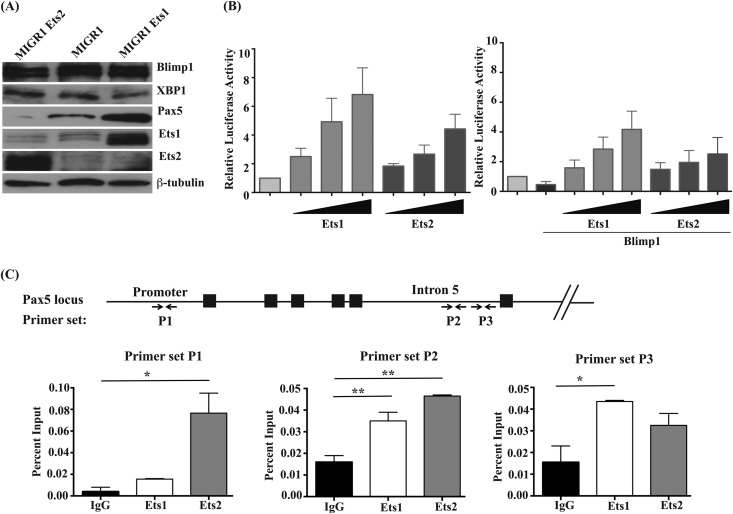
FIG 2.
Ets1 but not Ets2 stimulates Pax5 expression in differentiating B cells, although both can transactivate the gene. (A) Western blot analysis of Blimp1, XBP-1, Pax5, Ets1, and Ets2 in retrovirally infected B cells. Levels of β-tubulin are shown as a loading control. (B) A20 B lymphoma cells were transfected with the BSAP-Luc reporter gene construct (containing bp −1771 to +50 of the mouse Pax5 gene promoter sequences fused to a firefly luciferase reporter). Cells were cotransfected with various concentrations of pCMV-HA-Ets1 or pCMV-HA-Ets2 and also cotransfected pCMV-βgal as an internal control. In some samples, cells were also cotransfected with pCDNA3.1 Blimp1. Shown are the averages of relative luciferase (luc) activities (after normalization to β-galactosidase) from three independent experiments. (C) Chromatin immunoprecipitation analysis using splenic B cells purified from wild-type mice. Chromatin was immunoprecipitated with polyclonal rabbit anti-Ets1 or anti-Ets2 antibodies. Quantitative PCR was performed with primers specific to the mouse Pax5 promoter sequences or the mouse Pax5 B cell-specific enhancer located in intron 5 (as shown by arrows at the bottom). The percentage of input chromatin was calculated for each primer set. Shown are the averages ± SEM of two separate chromatin immunoprecipitation experiments.