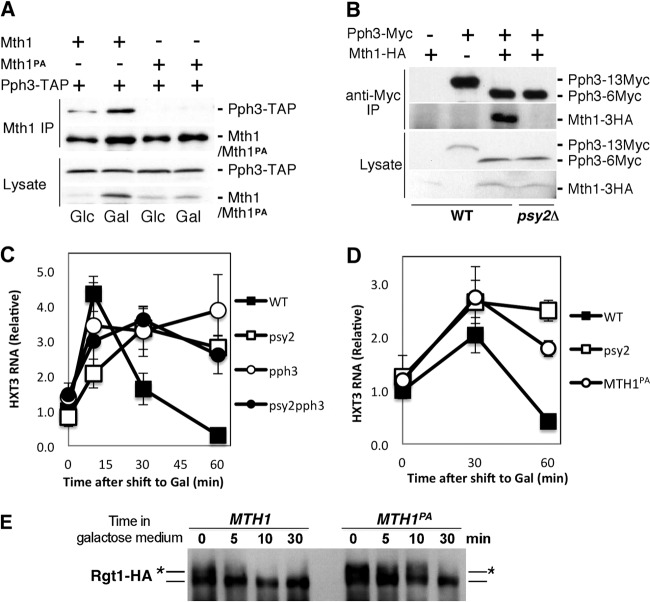
FIG 3.
The integrity of the Pph3-Psy2-Mth1 complex is critical for maintaining timely repression of HXT3 in response to glucose depletion. (A) Yeast cells expressing TAP-tagged Pph3 and HA-tagged Mth1/Mth1PA were subjected to coimmunoprecipitation analysis with anti-HA antibodies coupled to protein A-beads under the indicated conditions. The samples were then analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-HA to detect Mth1/Mth1PA-3HA and rabbit anti-mouse antibodies conjugated to horseradish peroxidase to detect Pph3-TAP, respectively. (B) Wild-type (WT) and psy2Δ mutant strains expressing Myc-tagged Pph3 and HA-tagged Mth1 from the endogenous loci were analyzed by coimmunoprecipitation. Pph3 expressed in the WT control is tagged with 13×Myc tag, whereas the other strains express Pph3 with a 6×Myc tag, which has more rapid gel mobility. (C) The repression of HXT3 gene upon glucose depletion in pph3Δ, psy2Δ, and pph3Δ psy2Δ cells was analyzed by quantitative RT-PCR using samples collected as described in Fig. 2B. (D and E) Yeast cells expressing the mth1PA mutant from the endogenous locus were analyzed by quantitative RT-PCR for HXT3 expression (D) and immunoblotting for Rgt1-HA (E) in comparison to WT cells at the times indicated.