FIG 4.
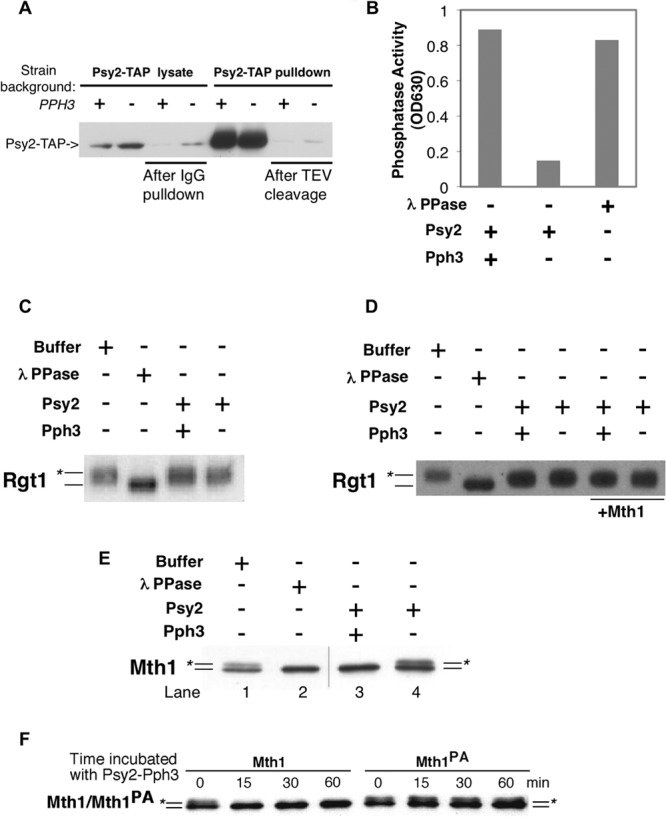
Mth1, but not Rgt1, is targeted by the Pph3-Psy2 phosphatase in vitro. (A) Psy2-TAP complex was purified from wild-type or pph3Δ strains by incubating the lysate with IgG-Sepharose, followed by TEV protease cleavage. The level of Psy2-TAP was detected by using rabbit anti-mouse antibody conjugated to horseradish peroxidase. The presence of Psy2-TAP before/after IgG pulldown and before and after TEV cleavage are shown sequentially from left to right. (B) Purified Psy2-Pph3 complex exhibited robust phosphatase activity. The results from an in vitro phosphate release assay using malachite green and a phosphopeptide substrate are shown. (C) FLAG-tagged Rgt1 purified from yeast was incubated with Psy2-TAP complex purified from wild-type (WT) or pph3Δ cells. Lambda phosphatase was used as a positive control. (D) The same experiment presented in panel C was repeated with the addition of the Mth1 protein. (E) Mth1 purified from a grr1-AAA yeast strain, which sequesters phosphorylated form of Mth1, was incubated with Psy2-TAP complex purified from WT or pph3Δ mutant cells as described in panel A. The position of the unphosphorylated Mth1 protein is indicated by a line, and the line marked with the asterisk denotes phosphorylated Mth1. The hairline marks the position of a splice between lanes from same gel. (F) Wild-type Mth1 and Mth1PA purified from grr1-AAA mutant cells were incubated with Pph3-Psy2 complex and samples were collected at the indicated time points. The positions of Mth1 and Mth1PA are labeled as in panel E.
