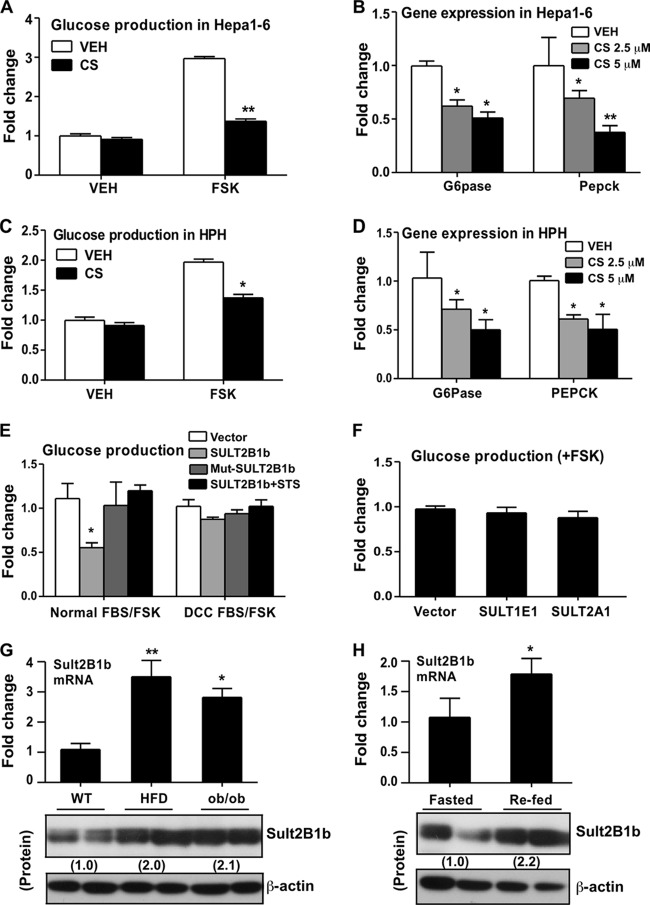
FIG 1.
Cholesterol sulfate (CS) and SULT2B1b inhibited gluconeogenesis in hepatic cells, and SULT2B1b was induced in obese mice and during the transition from the fasted to the fed state. (A) Glucose production in Hepa1-6 cells treated with a vehicle (VEH) or 5 μM CS for 24 h. (B) Relative expression of G6pase and Pepck mRNAs in Hepa1-6 cells treated with a vehicle or with CS at 2.5 or 5 μM for 24 h, as determined by real-time PCR analysis. (C) Glucose production in human primary hepatocytes (HPH) treated with a vehicle or 5 μM CS for 24 h. (D) Relative expression of G6pase and Pepck mRNAs in HPH treated with a vehicle or with CS at 2.5 or 5 μM for 24 h. (E) Glucose production in Hepa1-6 cells transfected with the indicated plasmids and combinations. Cells were maintained either in normal FBS or in FBS treated with dextran-coated charcoal (DCC FBS). (F) Glucose production in Hepa1-6 cells transfected with a vector, SULT1E1, or SULT2A1. (G) The hepatic expression of SULT2B1b mRNA (top) and protein (bottom) in HFD-fed WT mice and chow-fed ob/ob mice was measured by real-time PCR. (H) Hepatic expression of SULT2B1b mRNA (top) and protein (bottom) in fasted and refed mice. The relative expression of SULT2B1b protein in panels G and H is given below the bands. Results are means ± SD for three independent experiments or for 5 mice per group. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01.