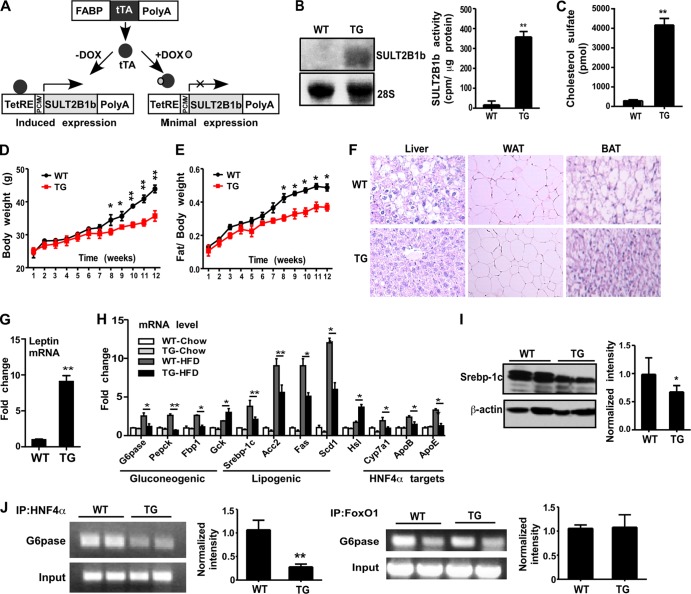
FIG 4.
Transgenic overexpression of SULT2B1b in the liver improved metabolic function. (A) Strategy for the creation of transgenic mice expressing SULT2B1b in the liver. PCMV, human cytomegalovirus (CMV) immediate-early promoter. (B) Northern blot analysis (left) and a SULT2B1b enzymatic assay using cholesterol as the substrate (right) were performed for wild-type (WT) and transgenic (TG) mice. (C) Levels of circulating CS. (D and E) Body weights (D) and fat-to-body weight ratios (E) of mice fed an HFD for the indicated periods. (F) H&E staining of the liver, white adipose tissue (WAT), and brown adipose tissue (BAT) in HFD-fed mice. (G) Relative expression of leptin mRNA in the WAT of HFD-fed mice. (H) Hepatic mRNA expression of gluconeogenic and lipogenic genes and HNF4α target genes in mice fed a chow diet or an HFD. (I) (Left) Expression of Srebp-1c protein as shown by Western blotting. (Right) Quantification of Western blotting data. (J) Recruitment of HNF4α (left) and FoxO1 (right) onto the G6pase gene promoter in the livers of HFD-fed mice as determined by ChIP assays. Bar graphs show the quantification of ChIP results. Results are means ± SD; n, 6 to 8 mice per group. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01.