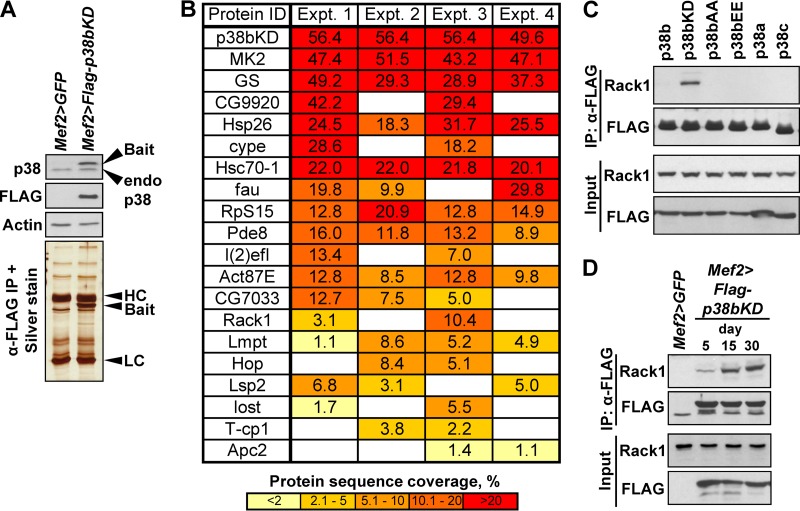
FIG 4.
Interaction proteomics identify Rack1 as a binding partner of p38bKD in adult thoracic muscle. (A) The Mef2>p38bKD transgenic flies express FLAG-p38bKD (bait) at a level comparable to endogenous p38b (Western blot, top). p38bKD and associated proteins are recovered from thorax extracts using a one-step affinity purification (silver stained gel, bottom) and subjected to LC-MS/MS analysis. HC, IgG heavy chain; LC, IgG light chain. (B) List of p38bKD interacting proteins identified by proteomics (see Materials and Methods for details). The results from four independent biological replicate (experiments 1 to 4) analyses are shown. The percent protein sequence coverage is shown for each interacting protein, with respective color coding shown below the table. (C) The interaction of Rack1 and p38b was confirmed by coimmunoprecipitation of endogenous Rack1 in S2 cells transiently transfected with FLAG-tagged wild-type p38 kinases, and three p38b mutants, p38bAA (T183A/Y185A), p38bEE (T183E/Y185E), and p38bKD (K53R). No interaction is observed between Rack1 and related kinases, p38a and p38c. Among the p38b constructs only the kinase-dead mutant shows robust interaction, a finding consistent with the substrate-trap model. (D) The p38bKD-Rack1 interaction is enhanced in aging flies. Coimmunoprecipitations were performed using thoraces of 5-, 15-, and 30-day-old Mef2>p38bKD flies, and the levels of endogenous Rack1 in precipitates were determined by Western blotting.