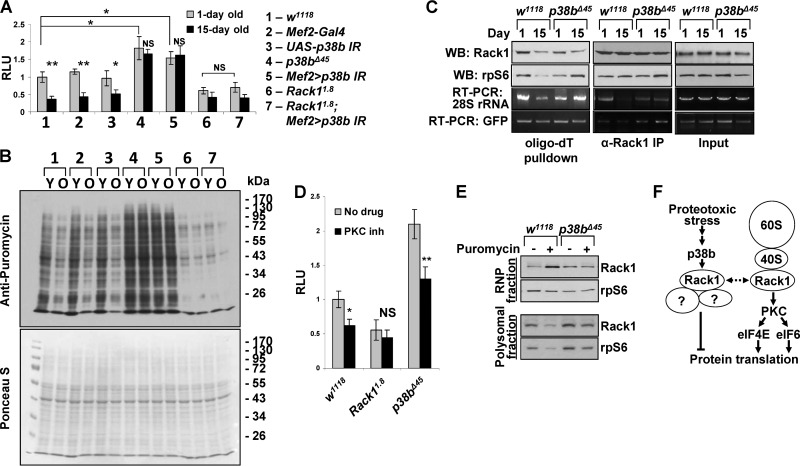
FIG 7.
p38b-Rack1 pathway controls translation rates in aging muscle. (A) In vitro translation assays were performed with thoracic extracts from 1- and 15-day-old flies using a synthetic firefly luciferase mRNA reporter (see Materials and Methods). Columns represent means ± the SD (n = 3; NS, not significant; *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01 [unpaired two-tailed Student t test]). (B) Translation rates were measured in vivo by feeding flies of the indicated genotypes (same as in panel A) 600 μM puromycin for 24 h. After treatment, thoracic extracts were analyzed by Western blotting with an antipuromycin antibody. Total protein was visualized by Ponceau-S staining. Y, young, 1-day-old flies; O, old, 15-day-old flies. (C) Changes in the association of Rack1 and ribosomal subunits with mRNA in aging wild-type and p38b-deficient flies were examined by oligo(dT) pulldown and anti-Rack1 immunoprecipitation. rpS6 and 28S rRNA were used as representative components of 40S and 60S ribosomal subunits. RNA levels were determined by semiquantitative RT-PCR. (D) The p38b-Rack1 and Rack1-PKC pathways appear to operate in parallel to affect translation rate in Drosophila muscle. Wild-type (w1118) and Rack1 (Rack11.8)- and p38b (p38bΔ45)-null mutants were fed chelerythrin chloride-supplemented food (PKC inh), followed by the measurement of translational activity in thoracic extracts in vitro (see Materials and Methods). p38b deficiency fails to counteract the repressive effect of PCK inhibition on translation. Columns represent means ± the SD (n = 3; NS, not significant; *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01 [unpaired two-tailed Student t test]). (E) p38b signaling is required for proteotoxic stress-induced dissociation of Rack1 from polysomes. Wild-type and p38b-null animals were treated with puromycin, and thoracic extracts were fractionated by using sucrose gradient centrifugation. Clear redistribution of Rack1 between the RNP (top of gradient) and polysome (bottom of gradient) fractions is observed in puromycin-fed wild-type flies. In p38b-null flies Rack1 remains largely associated with the polysomal fraction under proteotoxic stress. (F) Model depicting the mechanisms of Rack1-mediated translational control. A putative ribosome-unbound Rack1 complex that represses translation in response to p38 signaling is shown on the left.