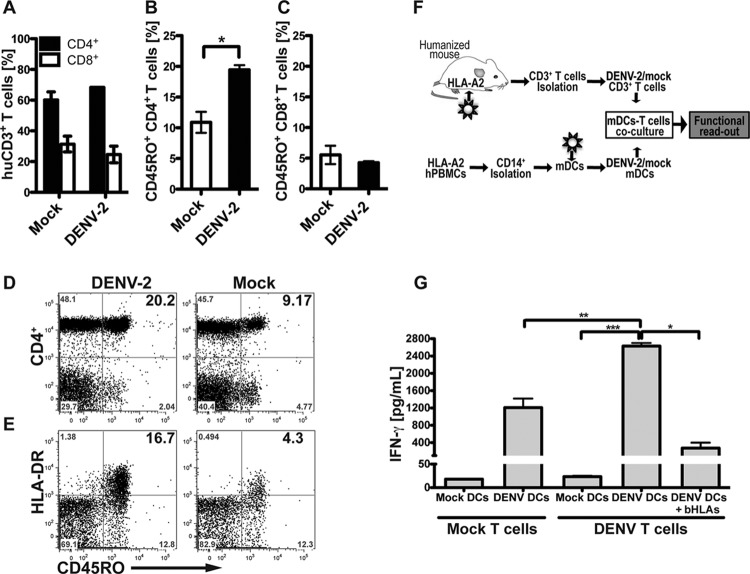
FIG 6.
DENV infection enhances the effector/memory phenotype and specific response to DENV antigens by T cells. (A) Frequency of human CD3+ T cell subsets CD4+ and CD8+ from peripheral blood of DENV- or mock-infected mice, analyzed by flow cytometry. (B and C) Frequency of effector/memory (CD45RO+) phenotype of CD4+ helper T cells (B) and CD8+ T cells (C). (D and E) Representative flow cytometry plots showing CD45RO+ expression on CD4+ T cells (D) and HLA-DR expression on CD45RO+ CD4+ effector helper T cells (E). For all panels, frequencies and activation levels of CD3+ T cells were analyzed at day 10 postinfection. Bold numbers in top right quadrants of each graph represent corresponding double-positive stained cells. (F) Schematic representation of the experimental layout. CD14+ monocytes were obtained from HLA-A2 blood donors and differentiated to mDC with a conditional medium containing IL-4 and GM-CSF for 5 days. mDC were then mock infected or DENV infected for 48 h and then mixed with T cells obtained from splenocytes from mock-infected or DENV-infected BLT-NOD/SCID mice. After 4 days in culture, human IFN-γ release in supernatants was measured as the functional readout. (G) Human IFN-γ secreted into supernatants by activated T cells, after 4 days of mDC-T cell coculture. Data were pooled from two independent experiments. Results are expressed in picograms per ml. Based on Student's t test, ***, P ≤ 0.0005; **, P ≤ 0.005; *, P ≤ v0.05.