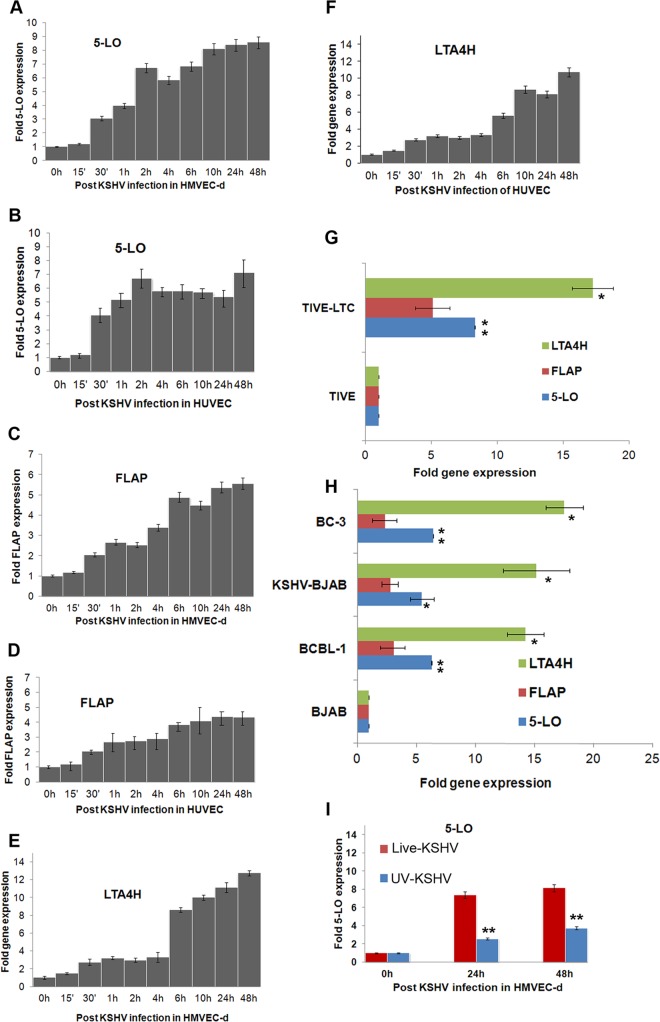
FIG 2.
Detection of 5LO pathway enzymes during de novo KSHV infection in latently infected ECs and in PEL cells. (A to F) Gene expression of 5LO pathway enzymes during primary infection of HMVEC-d and HUVEC. Cells grown to 80 to 90% confluence were serum starved for 8 h and infected with 30 DNA copies/cell of KSHV for different time points. At different times p.i. (up to 48 h), total RNA was isolated, DNase I treated, and then subjected to qRT-PCR using 5LO (A, B), FLAP (C, D), and LTA4H (E, F) gene-specific TaqMan primers. (G) Expression of LTA4H, FLAP, and 5LO in TIVE and TIVE-LTC cells. Cells were serum starved for 24 h and then used to prepare total RNA, and the expression of LTA4H, FLAP, and 5LO genes was analyzed. (H) Expression of LTA4H, FLAP, and 5LO genes in BCBL-1 BC-3, BJAB-KSHV, and BJAB cells. B cells grown to about 106 cells per ml were serum starved (0.2% FBS) for 8 h. Total RNA was isolated, DNase I treated, and then subjected to qRT-PCR using LTA4H, FLAP, and 5LO gene-specific TaqMan primers. Fold induction in panels A to F was calculated by considering induction in uninfected HMVEC-d (A, C, and E), HUVEC (B, D, and F), TIVE cells (G), and BJAB cells (H) to be 1-fold. (I) Expression of the gene for the 5LO enzyme during primary infection of HMVEC-d with 30 DNA copies/cell of live KSHV or UV-inactivated KSHV (UV-KSHV) for 24 h or 48 h. At different time points postinfection (24 h or 48 h), total RNA was isolated, DNase I treated, and then subjected to qRT-PCR using 5LO-specific TaqMan primers and ABI expression assays. Each bar represents the average ± SD of three independent experiments.