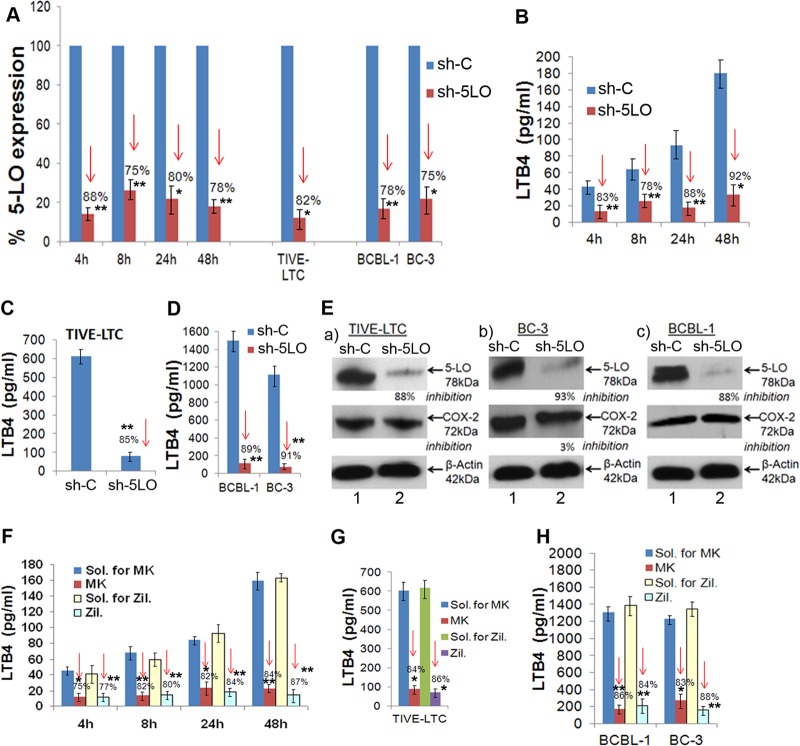
FIG 6.
5LO silencing or 5LO chemical inhibition reduces 5LO gene expression and LTB4 secretion. HMVEC-d were transduced with sh-C or sh-5LO at a multiplicity of infection of 10, as described previously (19). sh-C- or sh-5LO-transduced HMVEC-d were serum starved for 8 h and infected with KSHV for 4 h, 8 h, 24 h, and 48 h. RNA from these cells was analyzed by qRT-PCR for 5LO expression (A), and the supernatants were used to quantify LTB4 levels by ELISA (B). (A) Percent gene (5LO) expression by considering the expression in sh-C-transduced cells at the respective time points to be 100%. Similarly, 5LO gene expression was examined in sh-C- or sh-5LO-transduced TIVE-LTC, BCBL-1, and BC-3 cells. (C and D) Supernatants from sh-C or sh-5LO transduced TIVE-LTC cells (C) and BCBL-1 and BC-3 cells (D) were used to detect LTB4 secretion. (E) Lysates prepared from sh-C- or sh-5LO-transduced TIVE-LTC, BC-3, and BCBL-1 cells were tested for the protein levels of 5LO and COX-2. These blots were reprobed with anti-β-actin antibody to confirm equal loading. 5LO chemical inhibition reduces LTB4 secretion. HMVEC-d were pretreated with solvent for MK866 (MK), MK866, solvent for zileuton (Zil.), or zileuton for 1 h and then infected with 30 DNA copies KSHV/cell for different times by the methods described previously (19). (F) Supernatants were used to quantify LTB4 levels by ELISA. (G and H) Supernatants from solvent- or inhibitor-treated TIVE-LTC cells (G) and BCBL-1 and BC-3 cells (H) were used to detect LTB4. LTB4 levels in quadruplicate samples were measured, and values are presented in pg/ml. Each point represents the average ± SD from three independent experiments. The statistical analysis was carried out using a two-tailed Student's t test. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01. Red arrows facing down, percent inhibition.