FIG 4.
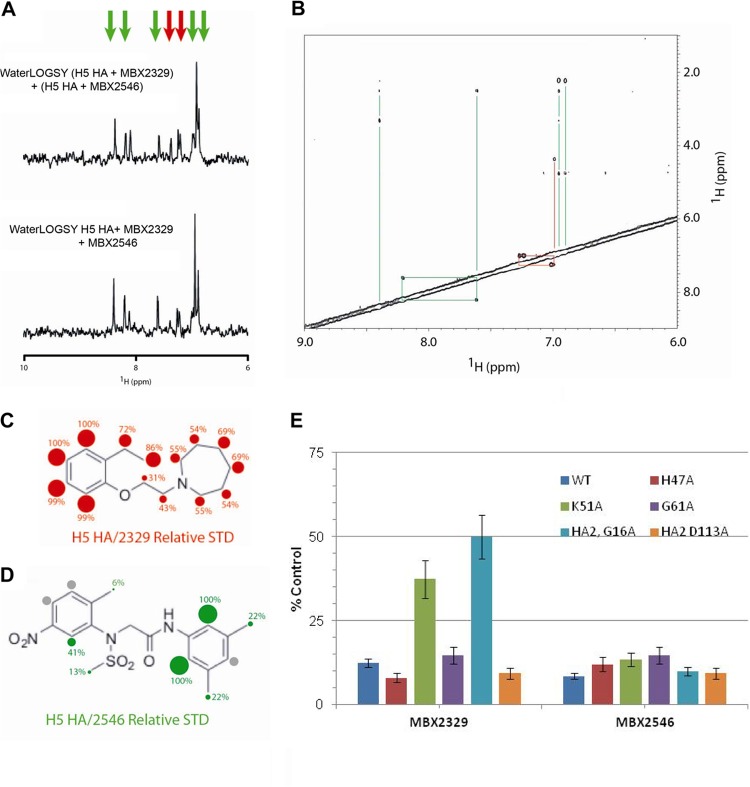
MBX2329 and MBX2546 bind to nonoverlapping sites on HA. (A) Competition assay performed between MBX2329 and MBX2546 for binding to influenza virus H5 HA by WaterLOGSY NMR. The top spectrum represents the sum of the WaterLOGSY of MBX2329 and H5 HA with the WaterLOGSY of MBX2546 and H5 HA. The bottom spectrum represents the WaterLOGSY signal in the presence of MBX2329, MBX2546, and H5 HA. The experimental conditions were 50 μM MBX2329 and/or 20 μM MBX2546 plus 0.2 μM HA in 20 mM PBS (pH 7.2) at 25°C, using a 900-MHz spectrometer with a mixing time of 1 s. (B) Two-dimensional NOESY of MBX2329 and MBX2546 in the presence of H5 HA. The lines represent the intramolecular NOE connectivities. The experimental conditions were 50 μM MBX2329, 50 μM MBX2546, and 0.2 μM HA in 20 mM PBS (pH 7.2) at 25°C, using a 900-MHz spectrometer with a mixing time of 1 s. (C and D) STD NMR studies to characterize the binding epitopes of MBX2329 (C) and MBX2546 (D) for H5 HA. The numbers and sizes of the spheres represent the intensity of the STD signal, which is related to the distance to the protein surface. For this set of experiments, the conditions were 50 μM MBX2329/MBX2546 with or without 0.2 μM HA in 20 mM PBS (pH 7.2) at 25°C, using a 900-MHz spectrometer with a saturation time of 1 s. (E) Effect of MBX2329 and MBX2546 on the infectivity of HIV/HA(H5) mutants. A549 cells were infected with mutant or wild-type HIV/HA(H5) with either MBX2329 or MBX2546 at 6.25 μM. Inhibition of infection by HIV/HA(H5) (or its mutants) was detected as a reduced luciferase signal. Each mutant was tested in triplicate; error bars indicate standard deviations. WT, wild type.