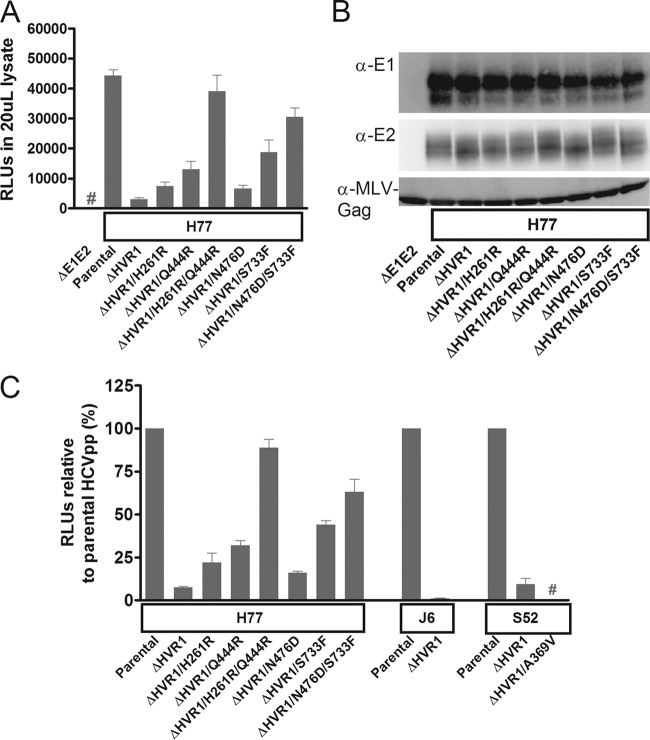
FIG 2.
Deletion of HVR1 from H77, J6, and S52 HCVpps decreased infectivity, while HVR1-related adaptive envelope mutations restored infectivity of H77ΔHVR1, but not of S52ΔHVR1, HCVpps. 293T cells were transfected as described in Materials and Methods to produce HCVpps with the indicated HCV envelope proteins. The HCVpps were used for infection of Huh7.5 cells, and infection was assessed by measuring the RLU of luciferase activity. (A) Mean RLU from 8 replicates in Huh7.5 cells following infection with the indicated HCVpps. The error bars indicate standard deviations (SD). #, the luciferase signal was below the cutoff. (B) Western blot of MLV-Gag and HCV envelope proteins, E1 and E2, from supernatants used in the infection experiment in panel A. (C) For each set of data (H77, J6, and S52), mean RLU normalized to the parental virus from three HCVpp experiments carried out with three independent batches of HCVpps are shown. Each experiment contained 4 or 8 independent luciferase measurements. RLU values from infections of Huh7.5 cells are normalized to the parental envelope protein control. The error bars indicate SEM. #, luciferase activity was below the cutoff. RLU (background subtracted) for H77, J6, and S52 without envelope mutations varied from 8,703 to 91,947, 2,561 to 55,469, and 95,499 to 2,844,709, respectively, among the three experiments.