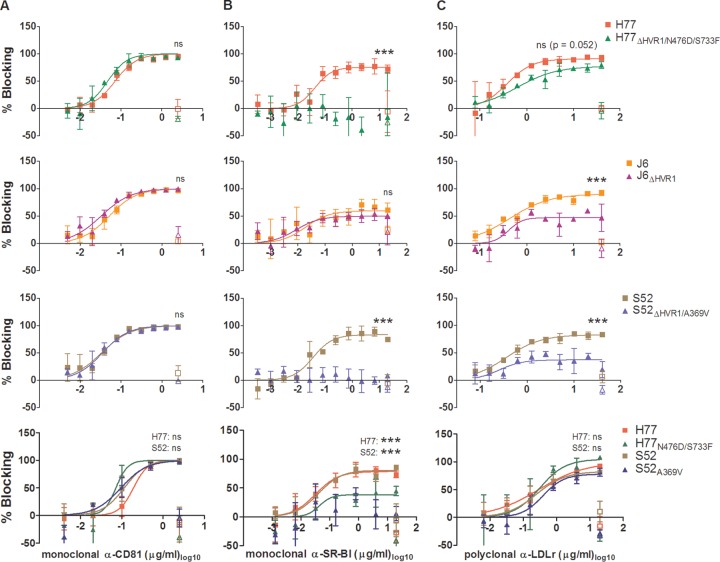
FIG 4.
Blocking of HCV receptors on Huh7.5 cells revealed that HVR1-deleted viruses had decreased SR-BI and LDLr dependency. Huh7.5 cells were plated in 96-well plates. The following day, the blocking antibody or a relevant control antibody was incubated with the cells for 1 h at each concentration in three replicates, also including 6 wells without antibody. Infection was carried out by 3 h of incubation with the indicated viruses; the cells were washed once, and FFU were visualized after an additional 45 h by HCV-specific immunostaining. (A) Anti-CD81 antibody JS81 blocking of HCV infection against the indicated viruses. (B) Anti-SR-BI antibody C16-71 blocking of HCV infection against the indicated viruses. (C) Anti-LDLr antibody AF2148 blocking of HCV infection against the indicated viruses. Blocking data are shown as dose-response curves, with the means and SD of three replicates at the given antibody dilution normalized to 6 replicates of virus only. The open symbols represent data for the control antibody only tested at the highest antibody concentration. Four-parameter nonlinear curve regression was used to fit a curve to the data points (Graphpad Prism, v4.03). Z-tests were used to compare the differences in maximum attained blocking for each antibody. In the three bottom panels, the pairwise comparisons were made between viruses of the same isolate with and without the indicated envelope mutations. ***, statistical significance at a P value of <0.001; ns, not statistically significant.