FIG 4.
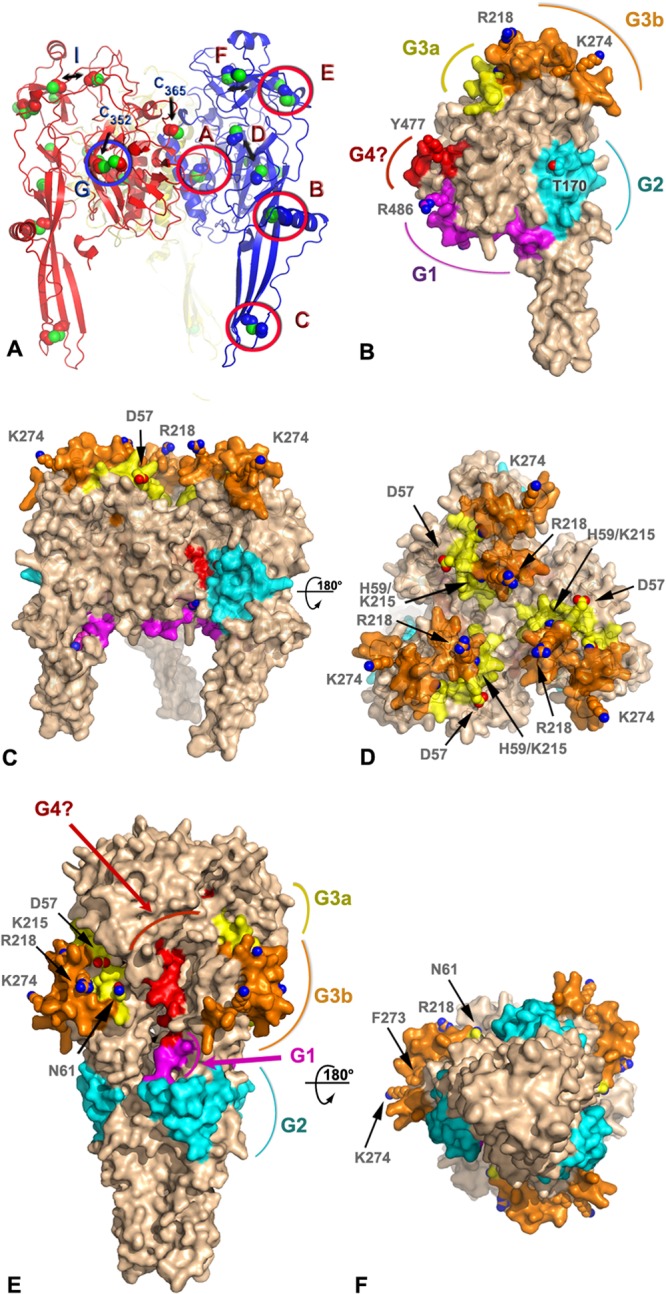
Model of antigenic sites on the prefusion and postfusion forms of the BEFV G trimer. (A) Ribbon representation of a homology model of BEFV G trimer derived by threading with the prefusion VSV G protein structure (PDB code 2J6J). The three subunits are shown in blue, red, and yellow with sulfur atoms in green. The side chains of the cysteine residues are shown as spheres. Disulfide bonds are labeled according to the nomenclature of Walker and Kongsuwan (25), and the residue number is indicated for the two free cysteines. Double arrows indicate cysteines that are expected to form disulfide bonds but are too far apart in the model. (B) Surface representation of a subunit of the BEFV G trimer approximately in the orientation of the subunit colored in blue in panel A. The antigenic sites G1, G2, G3a, and G3b and the putative G4 site are colored in magenta, cyan, yellow, orange, and red, respectively. The side chains of residues discussed in the text are shown as spheres and are labeled. The molecular surface around these residues has been omitted for clarity. (C and D) Orthogonal views of the BEFV G trimer in its prefusion conformation with the same representation and color scheme as that for panel B. The viral membrane is located at the bottom of the trimer in this orientation. (E and F) Orthogonal views of the BEFV G homology model derived by threading with the postfusion, trimeric structure of the VSV G protein (PDB code 2CMZ) with the same representation and color scheme as that for panel B.
