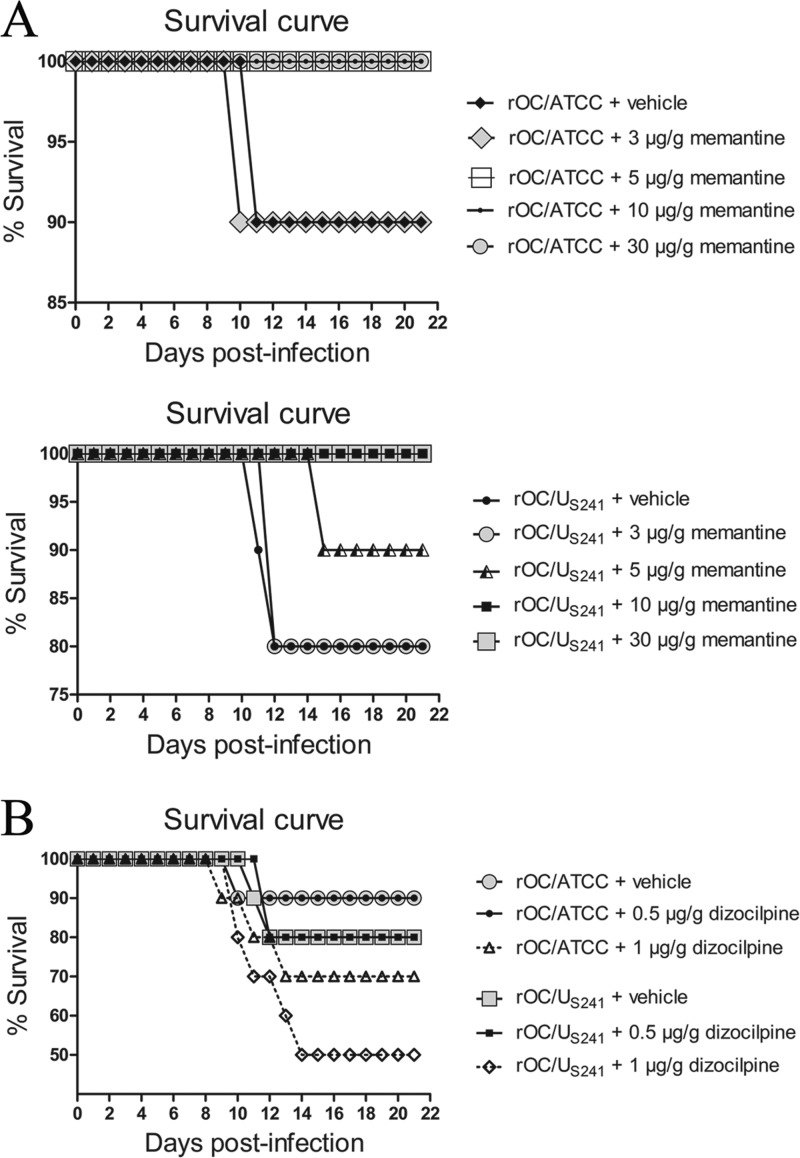
FIG 2.
Daily memantine treatment attenuates the mortality rates of infected mice compared to those achieved with dizocilpine and vehicle (control) treatment. Groups of 10 BALB/c mice infected with reference wild-type virus (rOC/ATCC) or S-mutant virus (rOC/US241) were treated daily with an intraperitoneal injection of a defined dose of memantine or dizocilpine or of PBS (vehicle). (A) Daily memantine treatment attenuated (doses, up to 5 μg/g) and totally suppressed (doses, 10 μg/g and above) the mortality rates for mice infected with either virus in a dose-dependent manner. (B) Daily dizocilpine treatment did not attenuate the mortality rates for mice infected with either virus. A higher dose of dizocilpine (1 μg/g) by itself increased the mortality rate. Results are representative of three independent experiments.