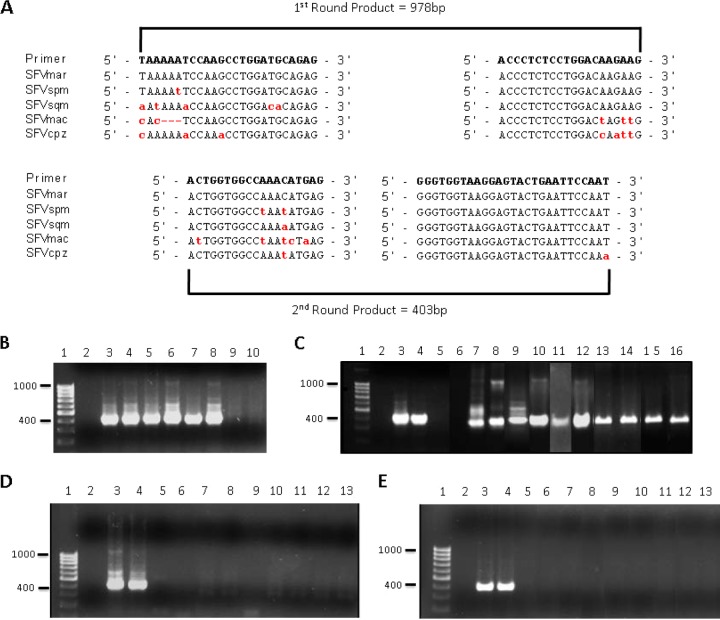
FIG 2.
Nested PCR detection of SFV DNA in New World monkey and human blood. (A) A set of nested PCR primers were designed to specifically amplify a region of the SFV pol gene from NWM. Alignment of available New World SFV sequences from marmoset, spider, and squirrel monkeys allowed the design of primers in highly conserved regions. The red, lowercase letters indicate nonconsensus nucleotides. The nested PCR protocol amplified a 978-bp DNA fragment in the first round of PCR and a 403-bp DNA fragment in the second round. (B to E) Nested PCRs were performed, and second-round PCR products were visualized using gel electrophoresis and ethidium bromide staining. (B) Sensitivity of the NWM Pol primers was assessed by using known amounts of the SFVspm pol gene in the plasmid pSFVsqu3′ added to 200 ng of genomic DNA isolated from uninfected HT1080 cells. Samples included a DNA molecular size marker (lane 1), a no-DNA control (lane 2), and 10 (lanes 3 and 4), 5 (lanes 5 and 6), 1 (lanes 7 and 8), or no (lanes 9 and 10) copy equivalents of SFVsqu3′ mixed with 200 ng of HT1080 genomic DNA. (C) The ability of the NWM pol primers to detect SFV DNA extracted from infected cells in culture and from blood of New World monkeys was examined. Samples included a DNA molecular size marker (lane 1); no-template control (lane 2); 10 (lane 3), 5 (lane 4), or 1 (lane 5) copy equivalents of the plasmid pSFVsqu3′; 200 ng of genomic DNA extracted from uninfected (lane 6); SFVsqu-infected (lane 7); SFVspm-infected (lane 8) or SFVmar-infected (lane 9) Cf2Th cells; 200 ng of genomic DNA extracted from the whole blood of captive squirrel monkeys 2120 (lane 10), 2809 (lane 11), and 4028 (lane 12) and wild monkeys from Costa Rica: Howler monkey AP170 (lane 13) and AP171 (lane 14), capuchin CC74 (lane 15), and squirrel monkey SO39 (lane 16). (D and E) The presence of New and Old World SFV DNA in the blood of antibody-positive APH individuals was determined. (D) Samples included a DNA molecular size marker (lane 1), a no-template control (lane 2), or 10 (lane 3), 5 (lane 4), or 1 (lane 5) copy equivalents of the plasmid pSFVsqu3′. (E) Additional samples for pSFV-1 included 200 ng of genomic DNA extracted from whole blood of APH 3 (lane 6), APH 10 (lane 7), APH 25 (lane 8), APH 48 (lane 9), APH 71 (lane 10), APH 75 (lane 11), APH 84 (lane 12), and APH 111 (lane 13). NWM SFV pol primers were used in panel D; previously described primers specific to OW SFV pol (55) were used in panel E.