FIG 6.
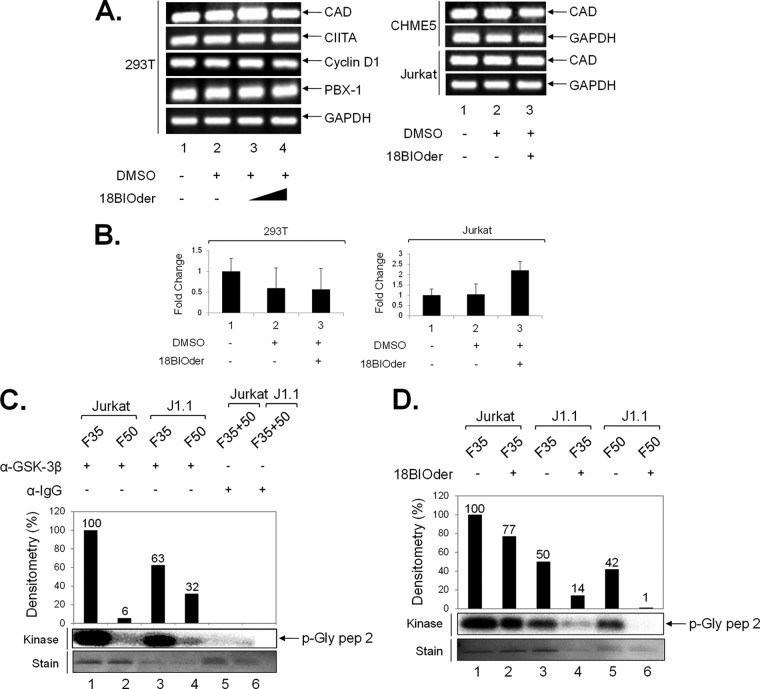
18BIOder does not inhibit cellular gene expression in the absence of Tat and is specific to GSK-3β. (A) Total RNA was isolated from cells treated with 18BIOder (1.0 and 10 μM for 293T cells and 1.0 μM for CHME5 and Jurkat cells) using RNeasy Mini Kit extraction. A total of 500 ng was used to generate cDNA with the iScript cDNA synthesis kit using oligo(dT) reverse primers. The primers for PCR were CAD, CIITA, cyclin D1, PBX-1, and GAPDH as a control. (B) A representative panel of intracellular RNA levels of PBX-1 were determined by qRT-PCR using total RNA extracted from cells shown in panel A. The error bars indicate standard deviations. (C) GSK-3β IPs from fractions 35 and 50 (250 μl each) were mixed with 5 μg of GSK-3β or IgG (control immunoprecipitation) antibodies overnight and washed the next day, first with RIPA buffer (1×) and then TNE and 0.1% NP-40 (2×), followed by kinase buffer (3×), prior to addition of substrate and [γ-32P]ATP. Samples were run on a gel, stained, destained (over 4 h), dried, and then exposed to a phosphorimager cassette. (D) IP/kinase reactions were treated with 18BIOder (10 nM) in vitro during the kinase reaction. Samples were run on a gel and exposed to a phosphorimager cassette. The kinase assay was quantified by densitometry and expressed as percent kinase activity compared to the immunoprecipitated Jurkat fraction 35 GSK-3β activity. (Bottom) Coomassie gels show p-Gly pep 2 substrate stains.