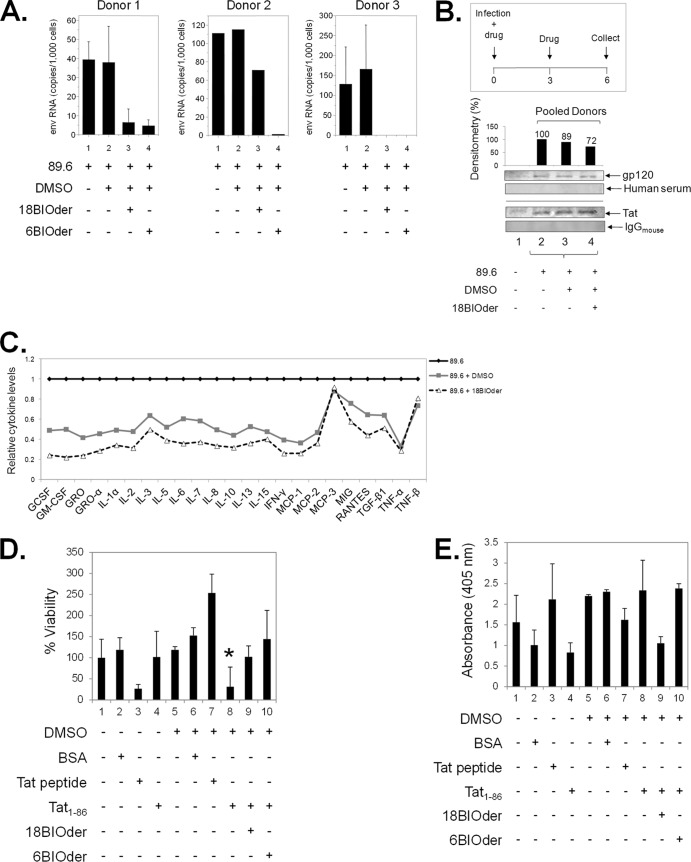
FIG 7.
18BIOder protects microglial and neuronal cultures from the HIV-1 Tat protein. (A) Primary macrophages from three donors were infected with HIV-1 89.6 by spinoculation. After overnight recovery, the cells were treated with DMSO or 10 μM 18BIOder or 6BIOder, and thereafter every 2 days postinfection (total, 3 treatments). The supernatants were collected, and virus production was measured by analyzing Env RNA copies using qRT-PCR at day 6 postinfection. Triplicate samples from donors 1 and 3 and a single sample from donor 2 were analyzed. Insufficient material was recovered from donor 2 for triplicate analysis. (B) Supernatants collected from the infected macrophages at day 6 postinfection as in panel A were pooled and subjected to nanoparticle capture of gp120 and Tat by using NT082 (Cibacron Blue F3G-A) and NT084 (Acid Black 48). Nanoparticle contents were resuspended in 10 μl Laemmli buffer and run on a gel. Membranes were immunoblotted with HIV-1-infected human immune serum (for gp120) and α-Tat mouse monoclonal antibody. Normal human serum and mouse IgG were used as isotype controls. Densitometry counts were performed for α-gp120 blotting, and the effects of 18Bioder were compared. Western blotting was performed in duplicate. (C) Supernatants from panel A were subjected to exosome purification using Exoquick reagent following the manufacturer's instructions. Exosome material obtained from the infected macrophage supernatants were analyzed for cytokine expression using a custom human cytokine array (RayBio Human Cytokine Array 1) following the manufacturer's instructions. (D) dAP-7 neuronal cells were differentiated for 6 days and treated with 18- or 6BIOder (0.1 μM) for 1 h at 39°C prior to 18 h of exposure to 500 nM Tat1-86. Cell viability was tested using a CellTiter-Glo assay to determine the cytoprotection effect of BIOders. The quantifications are based on triplicate experiments, and statistical analyses were performed between DMSO and Tat1-86 treatments and also between Tat1-86 and BIOder treatments using Student's t test, and a significant P value is marked by an asterisk. Transcriptionally inactive Tat peptide containing the essential basic domain (positive control) and BSA (negative control) were used. (E) dAP-7 cells were similarly treated as in panel D and analyzed for cell death (apoptosis) by measuring DNA fragmentation at 405-nm absorbance in cell lysates. The error bars indicate standard deviations.