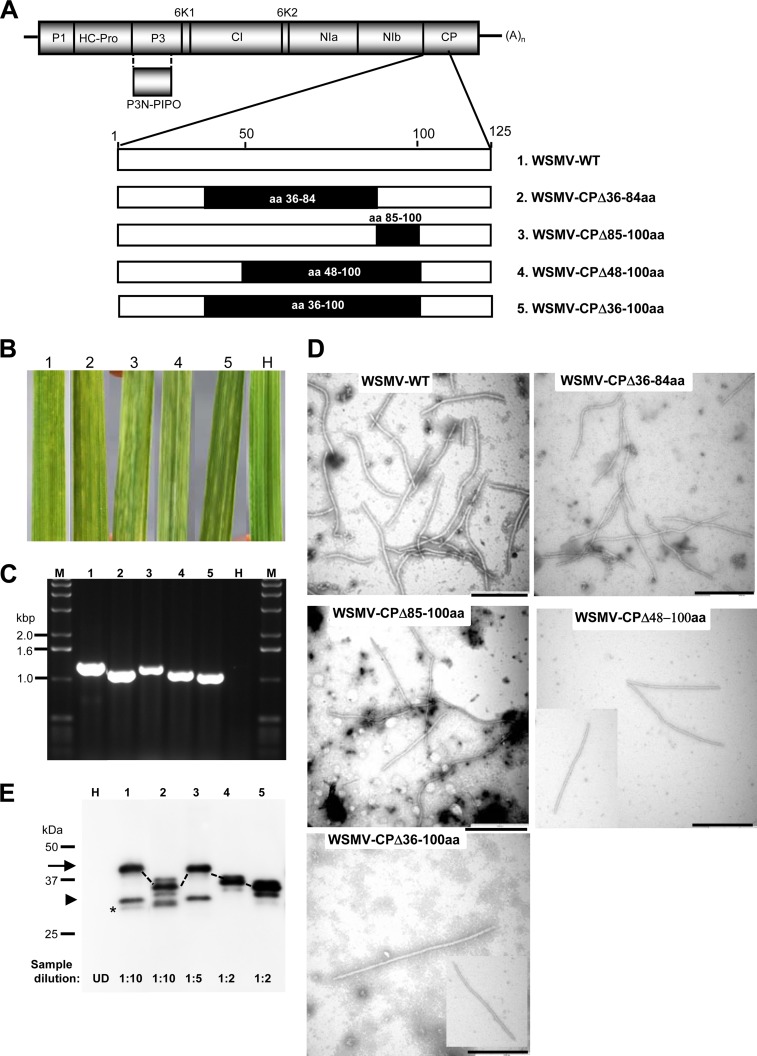
FIG 3.
WSMV with deletion of amino acids 36 to 100 in the CP systemically infects wheat. (A) Genomic organization of WSMV with proteins encoded by the polyprotein. An enlarged view of the N-terminal 125 amino acids is shown at the bottom of the schematic representation of the genome. The positions of the amino acids deleted from the CP are indicated with solid boxes, and the respective mutants are indicated at the right. WT, wild type. (B) Systemic symptoms induced by in vitro transcripts of WSMV CP deletion mutants on wheat. The numbers above the leaves correspond to the mutants indicated by number in panel A. Symptoms were induced by mutants 1 and 2 and mutants 3 to 5 at 9 and 16 dpi, respectively. Leaf H, a buffer-inoculated healthy wheat leaf. (C) RT-PCR amplification of the CP cistron from deletion mutant-infected wheat. The RT-PCR products were electrophoresed through a 1.0% agarose gel, and the numbers above the gel correspond to the mutants indicated by number in panel A. The sizes of the bands in the DNA ladder (lanes M) are indicated on the left. (D) Electron micrographs of virions of the wild-type virus and deletion mutants from systemically infected wheat. Bars, 500 nm. (E) Western blot analysis of partially purified virions from wheat leaves infected with the wild-type virus and CP deletion mutants. The numbers above the immunoblot correspond to the mutants indicated by number in panel A. The location of CP is indicated with an arrow, and the corresponding CP of the deletion mutants is marked with dotted lines. The positions of CP and the truncated 31- and 29-kDa CPs are indicated with an arrow, an arrowhead, and an asterisk, respectively. The protein size markers used in SDS-PAGE are indicated on the left. The dilution of the partially purified virions used for immunoblotting is indicated at the bottom of the blot. UD, undiluted.