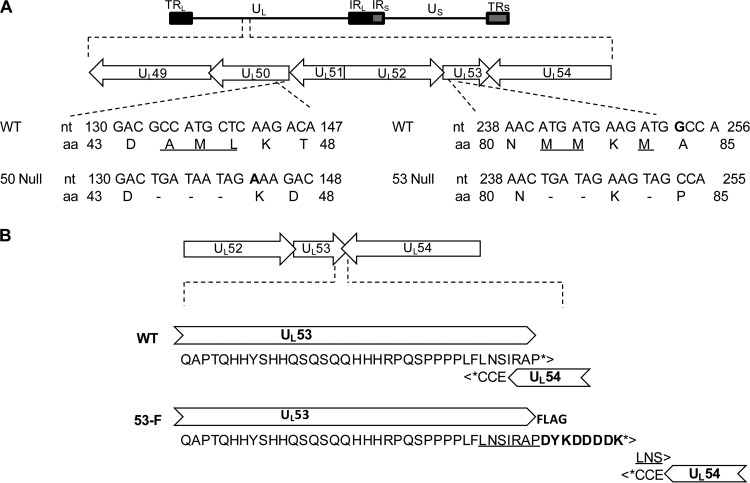
FIG 1.
Construction of HCMV UL50 and UL53 null mutants. (A) Organization of the HCMV genome. TRL, terminal repeat long; UL, unique long; IRL/S, internal repeat long and neighboring internal repeat short; US, unique short; TRS, terminal repeat short. Below the top schematic, the region of the viral genome from UL49 to UL54 is expanded, showing the overlaps between UL49 and UL50 and between UL52, UL53, and UL54. Below this, the mutations introduced into the UL50 and UL53 coding sequences for generation of 50N and 53N pBADGFP are shown. Amino acids that were mutated to stop codons (dashes) are underlined. Extra nucleotides are shown in bold. nt, nucleotide; aa, amino acid. (B) Construction of HCMV UL53-FLAG AD169-RV. Fusion of sequences encoding the FLAG tag to sequences encoding the C terminus of UL53 in a BAC of AD169 HCMV was performed. The UL52-UL53-UL54 region of the viral genome is expanded to show the details of the UL53 C-terminal sequence overlap with UL54 in the original wild-type (WT) genome. The stop codons for UL53 and UL54 are indicated by asterisks. The duplicated sequence is underlined, and the FLAG sequence is indicated in bold.