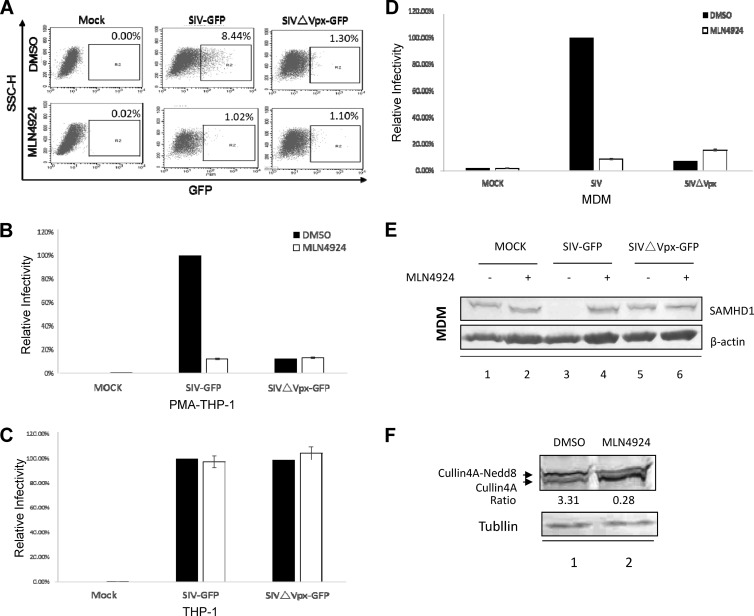
FIG 2.
Inhibition of SIV infection in macrophages by MLN4924. (A) MLN4924 is a highly effective inhibitor of Vpx-dependent SIVmac infection in PMA-treated THP-1 cells. Human monocytic THP-1 cells were stimulated with PMA (100 ng/ml for 48 h) and then treated with 300 nM MLN4924 or DMSO for 12 h. The two groups of treated cells were then infected with an equivalent amount of SIVmac239-GFP or SIVmacΔVpxGFP VLPs. The percentage of GFP-positive cells was determined by flow cytometry. Representative flow cytometry data are shown. (B) The rate of SIVmac239-GFP virus infection in the absence of MLN4924 was set to 100%. The bar charts are representative of three independent experiments, and the error bars indicate the standard deviations of three replicates within one experiment. (C) MLN4924 treatment had little effect on SIVmac infection in undifferentiated THP-1 cells. (D) MLN4924 is a highly effective inhibitor of SIVmac infection in primary macrophages. Primary macrophages were isolated and infected with SIVmac or SIVmacΔVpx viruses as previously described (26). Virus infection was determined by monitoring GFP-positive cells 2 days after infection. (E) Effect of MLN4924 treatment on SAMHD1 expression during SIVmac infection of primary macrophages. Cell extracts were harvested 2 days after infection and analyzed by SDS-PAGE, followed by immunoblotting with anti-SAMHD1 antibody to detect SAMHD1. β-Actin was used as the loading control. (F) Effect of MLN4924 treatment on Cullin4A expression. Endogenous Cullin4A from SIVmac virus-infected U937/SAMHD1 cells treated with MLN4924 or DMSO was detected with an anti-Cullin4A antibody from Abcam. Tubulin was used as the loading control.