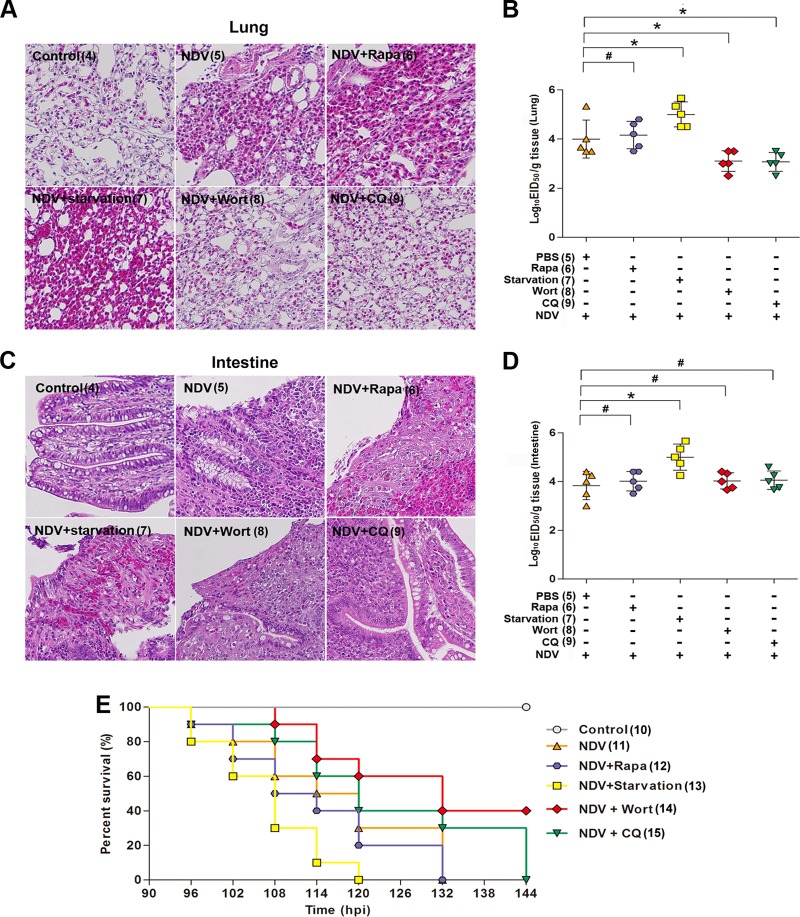
FIG 6.
Regulation of autophagy affects NDV production and pathogenesis in vivo. Thirty 7-day-old SPF chickens were randomly divided into 6 groups of 5. In vivo drug experiments were carried out as described previously (27). The chickens in groups 5, 6, 8, and 9 were treated with PBS, rapamycin (2 mg/kg), wortmannin (2 mg/kg), or CQ (20 mg/kg) intramuscularly for 5 times at 2 h before virus inoculation as well as 2 h, 12 h, 24 h, and 36 h after virus inoculation, respectively. The chickens in group 7 were treated with starvation by being deprived of food for 48 h but had free access to drinking water. The chickens in groups 5 to 9 were infected intranasally with NDV strain Herts/33 at 106 50% egg infectious doses (EID50). The chickens in group 4, as controls, received no treatment. At 48 h posttreatment, chickens were sacrificed and tissues were collected for measurement of virus titers (EID50). The lungs and intestines were subjected to histopathological observation with hematoxylin and eosin staining. (A and C) Hematoxylin and eosin staining of cells in chicken lung (A) and intestine (C) infected with NDV Herts/33 in the absence or presence of either rapamycin, wortmannin, or CQ, respectively. Treatment with 48-h starvation was used as a positive control. Images are representative of three chickens. (B and D) Viral titers in chicken lung (B) and intestine (D) separated from five chickens in each group were expressed as EID50 per milliliter. Data are presented as the virus titers in tissues from five chickens. Significance is analyzed with two-tailed Student's t test. *, P ≤ 0.05; #, P ≥ 0.05. (E) Survival rates of chickens that were treated with rapamycin, wortmannin, or CQ before and after being infected with NDV Herts/33 (n = 10 chickens). Sixty 7-day-old SPF chickens were randomly divided into 6 groups of 10. The treatments for chickens in groups 10 to 15 were the same as those for chickens in groups 4 to 9, respectively. After treatment, the chickens in groups 11 to 15 were infected intranasally with NDV strain Herts/33 at 104 EID50. The survival rates of chickens in each group were recorded for 6 days. Chickens in group 13 were fed every other day but had free access to drinking water. The numbers in parentheses represent the group numbers.