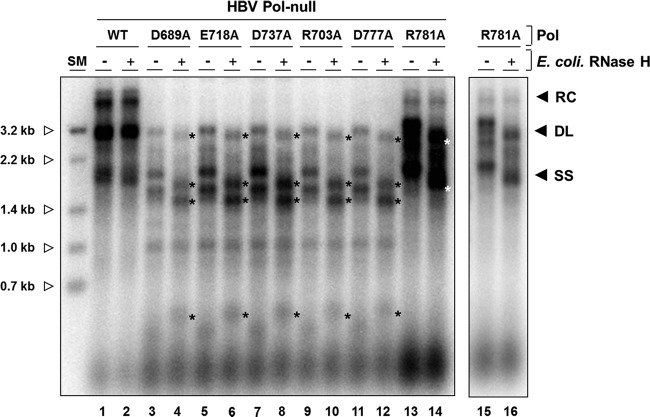
FIG 7.
Three single mutants have a defect in RNase H activity. Cells were cotransfected with an HBV P-null replicon construct along with WT Pol or an individual single substitution mutant as indicated. Approximately 1/10 (WT) or 3/10 (each mutant) of the capsid-associated DNA isolated from a 60-mm plate was analyzed by Southern blotting. DNA samples were either left untreated or subjected to E. coli RNase H treatment at 37°C for 20 min. Longer RNase H treatment and higher RNase H concentrations had no effect on migration. After treatment, each sample was immediately separated on a 1.2% agarose gel (14 by 12 cm). Asterisks to the right of labeled bands indicate newly appearing DNA forms following exogenous RNase H treatment. The intensities of bands (*) shifted upon the RNase H treatment were reduced to 90% (D689A), 93% (E718A), 92% (D737A), 95% (R703A), 93% (D777A), and 90% (R781A). Size markers (0.7 kb to 3.2 kb) were generated by restriction enzyme digestion of full-length HBV genome (open arrowhead). The results shown in lanes 15 and 16 are short exposures of lanes 13 and 14.