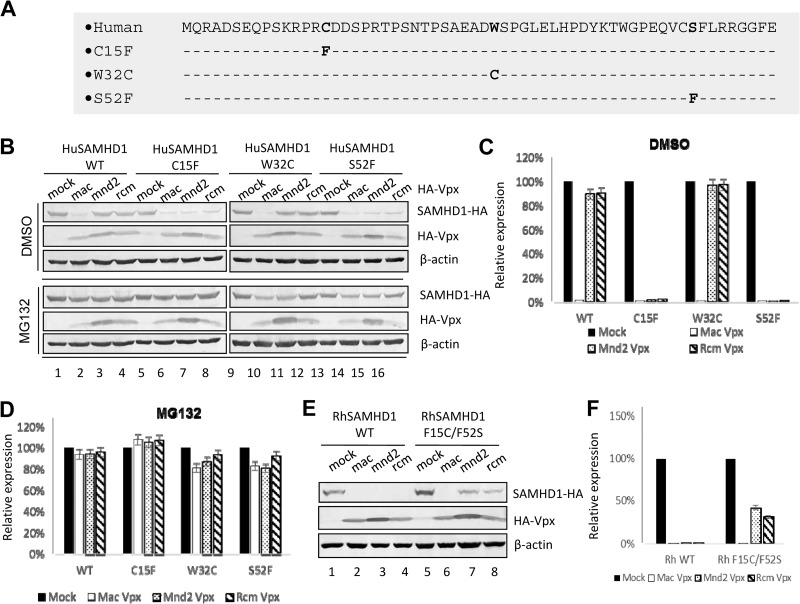
FIG 5.
Influence of F15 and F52 substitutions in Hu SAMHD1 on Vpx-mediated degradation. (A) Schematic representation of Hu SAMHD1 mutant constructs. (B to D) Effects of Hu SAMHD1 mutations on Vpx-induced degradation. Expression vectors for HA-tagged WT and C15F, W32C, and S52F mutant Hu SAMHD1 were coexpressed with expression vectors for the indicated HA-tagged Vpx in HEK293T cells. Cell extracts were harvested 48 h later and analyzed by SDS-PAGE, followed by immunoblotting to detect SAMHD1-HA and HA-Vpx. β-Actin was used as the loading control. Expression vectors for HA-tagged Hu SAMHD1 mutant proteins were coexpressed with HA-tagged Vpx in HEK293T cells. DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide. (E and F) Effects of Rh SAMHD1 mutations on degradation induced by diverse Vpx proteins. HA-tagged WT or F15C/F52S mutant Rh SAMHD1 was coexpressed with the indicated expression vector for HA-tagged Vpx or the empty vector in HEK293T cells. Cell extracts were harvested 48 h later and analyzed by SDS-PAGE, followed by immunoblotting to detect SAMHD1-HA and HA-Vpx; β-actin was used as the loading control. The data shown represent one of three independent experiments. Error bars represent the standard deviation of the mean of triplicate samples.