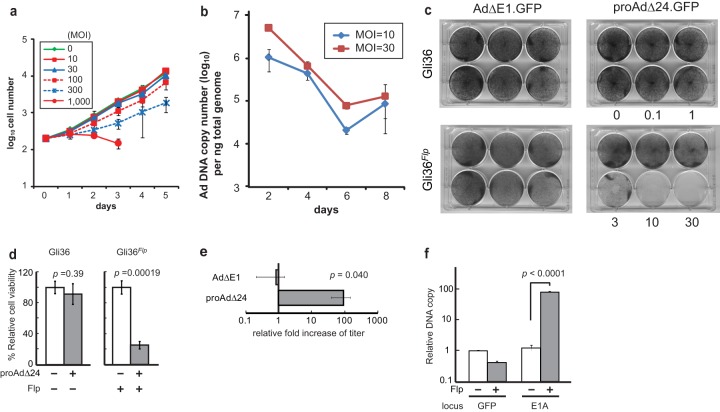
FIG 2.
(a) Gli36 cells were cultured for 5 days, following proAdΔ24.GFP infection at MOIs that ranged between 10 and 1,000. Viable cells were counted by trypan blue exclusion assay. (b) Real-time PCR analysis of proAdΔ24.GFP DNA was performed, using genomic DNA isolated from cultured Gli36 cells, at indicated times after infection with proAdΔ24.GFP at an MOI of 10 or 30. (c) Gli36 or Gli36Flp cells, grown on 6-well plates to a density of 5 × 104, were infected with RD AdΔE1.GFP or proAdΔ24.GFP at MOIs of 0.1 to 30. Crystal violet staining was carried out 7 days later. (d) Cell viability of Gli36 and Gli36Flp cells, 3 dpi with proAdΔ24.GFP (MOI, 10). Viable cells were counted using the trypan blue exclusion assay. (e) AdΔE1 or proAdΔ24.GFP viral titers were assayed 2 dpi of Gli36 and Gli36Flp cells (MOI, 10). Data are presented as means ± SEM, based on independently performed triplicate samples. (f) Real-time quantitative PCR analysis of E1A and GFP gene copy numbers from viral DNA recovered from proAdΔ24.GFP-infected Gli36 (Flp−) or Gli36Flp (Flp+) cell lysates treated with DNase I, followed by proteinase K. Data are presented as means ± standard deviations (SD) of triplicate samples. The experiment is representative of multiply performed experiments.