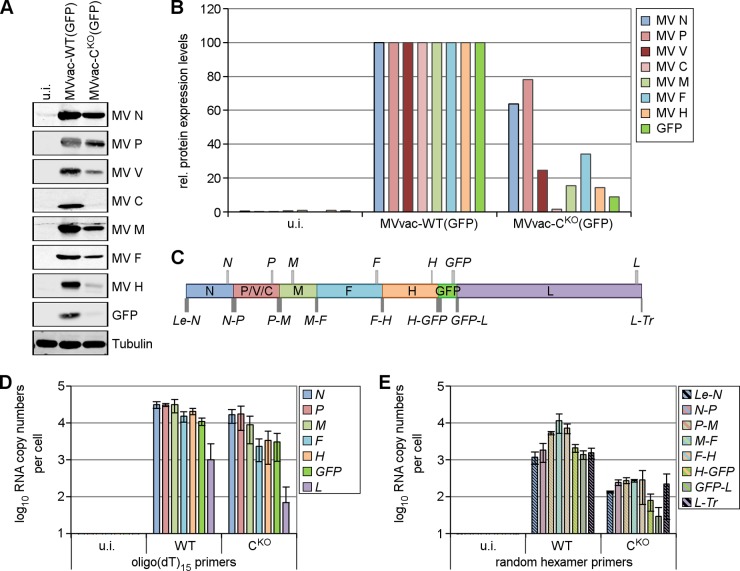
FIG 6.
Knockout of C protein slows viral macromolecular synthesis and results in a steeper transcription gradient. HeLa CONkd cells were infected with parental MVvac-WT(GFP) or mutant MVvac-CKO(GFP) virus or left uninfected (u.i.). Cells were harvested at 48 h after infection. (A) Immunoblot analysis with antibodies directed against the indicated viral and cellular proteins. Blots are representative of three independent experiments. (B) Quantification of the proteins from panel A. Protein levels were normalized to the corresponding tubulin levels in each lane and are relative to the levels of MVvac-WT(GFP)-infected cells, which were set as 100% for each protein. (C) Schematic representation of the genome organization of MVvac-WT(GFP). The relative size and location of the viral gene-specific (light-gray boxes) and intercistronic (dark-gray boxes) qPCR products are shown. (D) qPCR analysis of viral mRNA from infected cells using cDNA prepared with oligo(dT)15 primers. (E) qPCR analysis of intercistronic viral sequences from infected cells using cDNA prepared with random hexamer primers. The resulting cDNAs were analyzed for product copy number as described in Materials and Methods. Data shown are average numbers ± standard deviations from three independent experiments.