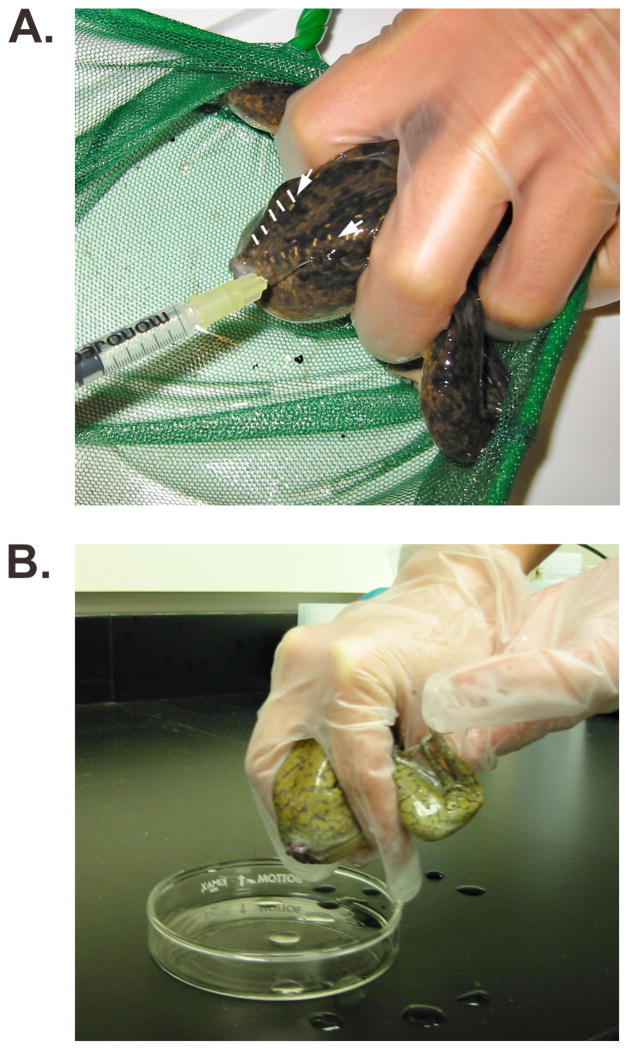
Figure 3.4. Spawning eggs from a female frog.
(A) Priming a mature female by injection of human chorionic gonadotropin into the dorsal lymph sac on the posterior aspect of the frog. The injection needle is inserted just lateral to the V-shaped lateral line sutures (white arrows; dashed white lines demarcate the sutures on the left side of the frog’s back). The head and eyes of the frog are covered with the palm of the hand (out of view) to reduce stress and the frog is immobilized by using a net to prevent forward motion and by holding the legs forward with two fingers. (B) Spawning of a female frog. The frog is held as described above, using the opposite hand, instead of the net, to provide additional stability.