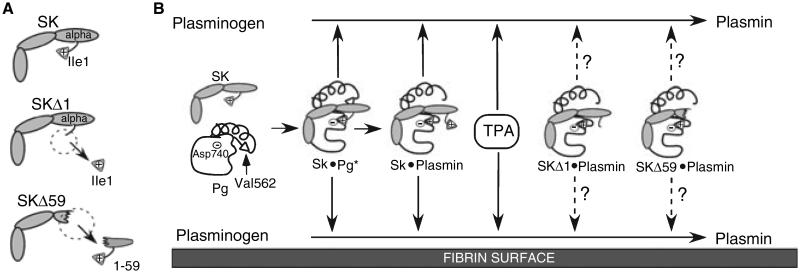
Fig. 1.
Schema of Pg activation by different PAs. (A) Schematic structure of SK, SKΔ1 and SKΔ59. (B) The activation of Pg to plasmin in solution (top) and on the fibrin surface (bottom) is shown. The amino acids involved in non-proteolytic activation of Pg by SK (SK isoleucine 1 (Ile 1), Pg aspartic acid 740 (Asp 740)) and the proteolytic generation of plasmin by other PAs (Pg valine 562 (Val 562) and Pg Asp 740) are indicated. Arrows with solid lines indicate known activity; arrows with dashed lines indicate potential activity.