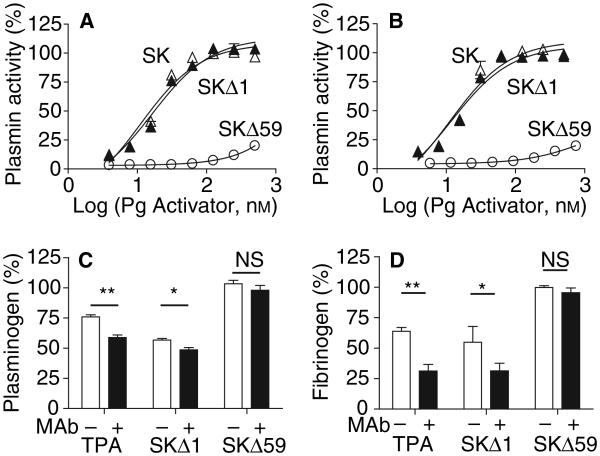
Fig. 3.
Effect of α2AP on the activity and fibrin-targeting of SKΔ1·plasmin, SKΔ59·plasmin and SK·plasmin. Resistance to inhibition by human (A) or mouse (B) α2AP. SKΔ1, SKΔ59 or SK (0–750 nM) were preincubated with human plasmin (12 nM) in 50 mM Tris–HCl, 100 mM NaCl, pH 7.4, for 10 min at 25 °C prior to addition of α2-AP (15 nM). After 10 min, residual plasmin activity was measured at 37 °C. (C,D) Effect of α2AP neutralization on Pg (C) and fibrinogen (D) consumption in human plasma treated with PAs. TPA (15 nM), SKΔ1 (15 nM) or SKΔ59 (100 nM) was added to human plasma with (filled bars) or without (clear bars) an antibody inhibitor of α2AP [1 μM, (26)] for 2 h at 37 °C. Residual Pg and fibrinogen concentrations were determined as described above. The means ± SEM are shown. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01, NS- not significant.