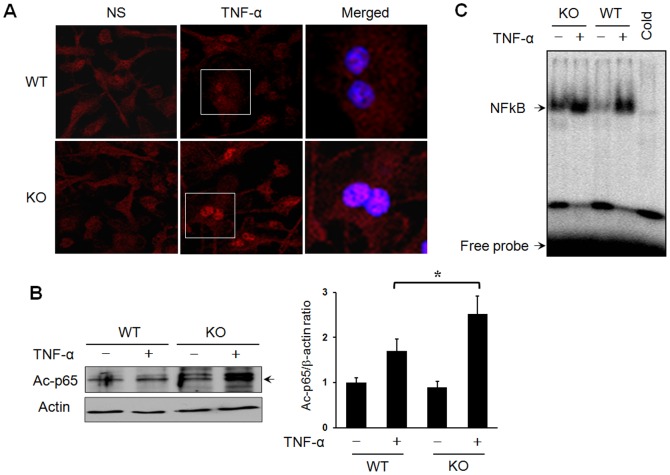
Figure 4. SIRT1 deficiency induces hyperactivation of NF-κB in BMMs.
BMMs were cultured from mSIRT1 or WT mice and stimulated with TNF-α (10 ng/ml) for 1 h. (A) Immunostaining for acetylated p65 showed that loss of SIRT1 resulted in higher and sustained levels of acetylated p65 in the nuclei of macrophages following TNF-α treatment. (B) The levels of acetylated p65 were analyzed by Western blotting. Representative blot shown is from one of the three independent experiments with similar results. Values = mean ± SE, *p<0.05 vs. WT. (C) The DNA binding activity of NF-κB was analyzed by EMSA.