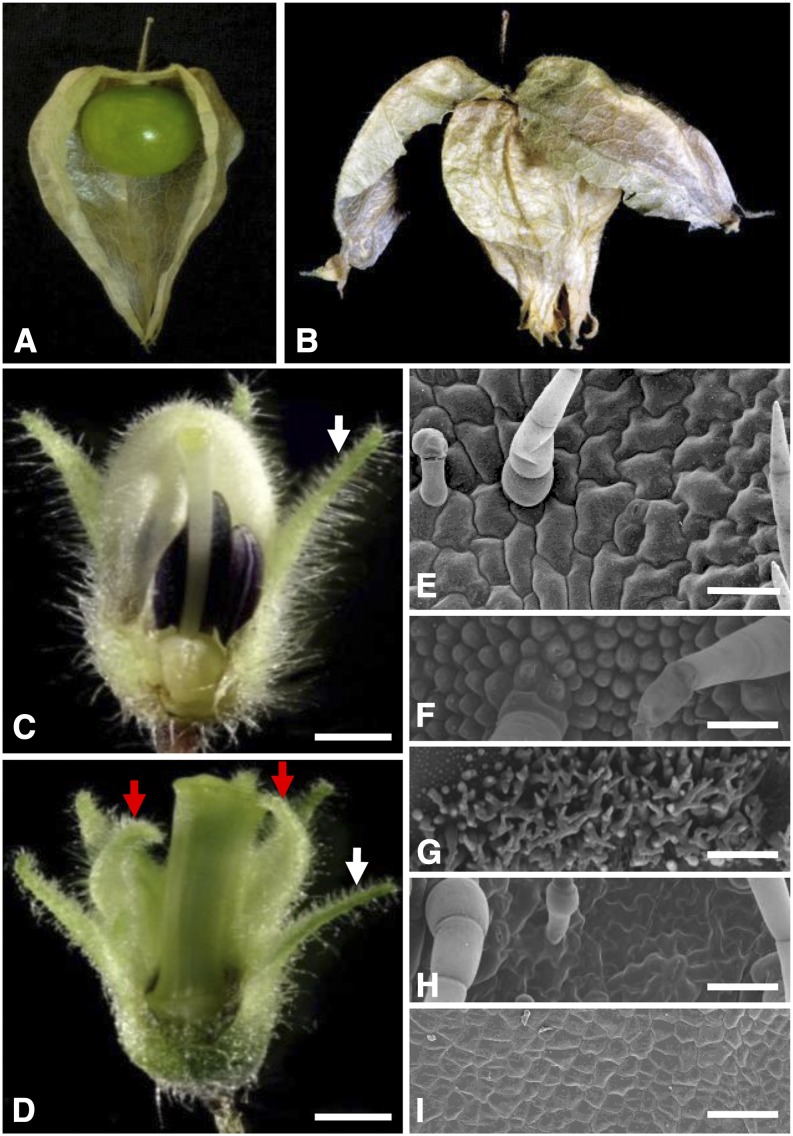
Figure 1.
Floral phenotypic analyses of the doll1 mutant. A, A wild-type fruit. Part of the ICS was removed to show the berry inside. B, A fruit from the doll1 mutant. The first layer of the lantern was broken to show the second layered lantern. C, A wild-type flower. D, A mutated flower. Parts of the vegetative organs of the flower were removed to show the reproductive structures. White arrows indicate the tip of the calyx, while the red arrows indicate the tip of the transformed calyx in the mutated flower. Bars = 1 mm. E, Epidermal cells on the abaxial zone proximal to the tip of the calyx. F, Epidermal cells on the abaxial tip zone of the corolla from a wild-type flower. G, Epidermal cells on the adaxial base of the corolla from a wild-type flower. H, Epidermal cells on abaxial tip zone of the second whorl of the mutated flower. I, Epidermal cells on adaxial base zone of the second whorl of the mutated flower. Bars = 100 um.