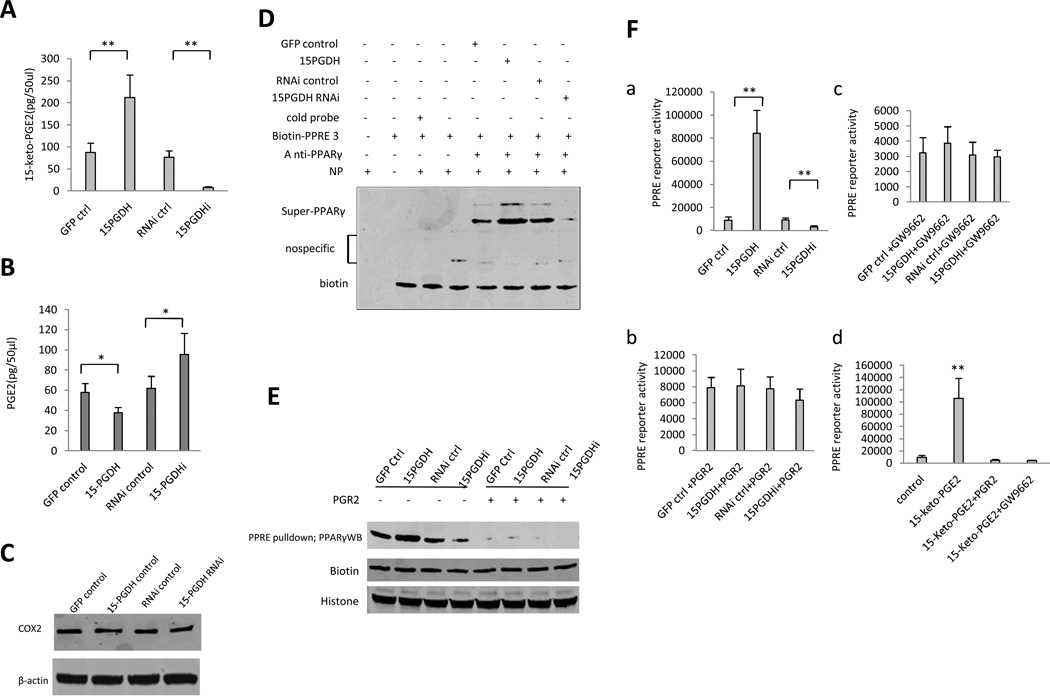
Figure 4. 15-PGDH-derived 15-keto-PGE2 activates PPARγ in HCC cells.
A. Enzyme immunoassay (EIA) for 15-keto-PGE2 metabolite in Huh7 stable cell lines. The data are presented as mean±SEM (**p < 0.01 compared to corresponding control).
B. Enzyme immunoassay (EIA) for PGE2 in Huh7 stable cell lines. The data are presented as mean±SEM (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01).
C. Western blotting for COX-2 in Huh7 cells with stable overexpression or knockdown of 15-PGDH. β-actin was used as the internal control.
D. PPARγ super-EMSA analysis using PPRE probe in Huh7 stable cell lines.
E. DNA pulldown in Huh7 stable cell lines. Biotin and histone were used as pulldown and loading controls.
F. PPRE-luciferase activity assay. a PPRE luciferase reporter activity in Huh7 stable cell lines (**p < 0.01 compared to corresponding control). b PPRE luciferase reporter activity in Huh7 stable cell lines with cotransfection of pCMV6-entry-PGR2 (Origene). c PPRE luciferase reporter activity in Huh7 stable cell lines treated with GW9662 (10µM). d PPRE luciferase reporter activity in wild type Huh7 cells treated with DMSO and 15-keto-PGE2 (10µM, Cayman Chemicals) (with or without PGR2 overexpression or 10µM GW9662 treatment).